Circulating microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction
- PMID: 20534597
- PMCID: PMC2980809
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq167
Circulating microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction
Abstract
Aims: Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) may represent a novel class of biomarkers; therefore, we examined whether acute myocardial infarction (MI) modulates miRNAs plasma levels in humans and mice.
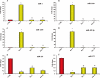
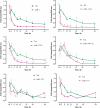
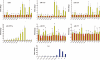
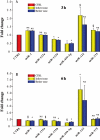
Methods and results: Healthy donors (n = 17) and patients (n = 33) with acute ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) were evaluated. In one cohort (n = 25), the first plasma sample was obtained 517 ± 309 min after the onset of MI symptoms and after coronary reperfusion with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI); miR-1, -133a, -133b, and -499-5p were ~15- to 140-fold control, whereas miR-122 and -375 were ~87-90% lower than control; 5 days later, miR-1, -133a, -133b, -499-5p, and -375 were back to baseline, whereas miR-122 remained lower than control through Day 30. In additional patients (n = 8; four treated with thrombolysis and four with PCI), miRNAs and troponin I (TnI) were quantified simultaneously starting 156 ± 72 min after the onset of symptoms and at different times thereafter. Peak miR-1, -133a, and -133b expression and TnI level occurred at a similar time, whereas miR-499-5p exhibited a slower time course. In mice, miRNAs plasma levels and TnI were measured 15 min after coronary ligation and at different times thereafter. The behaviour of miR-1, -133a, -133b, and -499-5p was similar to STEMI patients; further, reciprocal changes in the expression levels of these miRNAs were found in cardiac tissue 3-6 h after coronary ligation. In contrast, miR-122 and -375 exhibited minor changes and no significant modulation. In mice with acute hind-limb ischaemia, there was no increase in the plasma level of the above miRNAs.
Conclusion: Acute MI up-regulated miR-1, -133a, -133b, and -499-5p plasma levels, both in humans and mice, whereas miR-122 and -375 were lower than control only in STEMI patients. These miRNAs represent novel biomarkers of cardiac damage.
Figures

Comment in
-
Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases?Eur Heart J. 2010 Nov;31(22):2705-7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq221. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Eur Heart J. 2010. PMID: 20605798 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- miRBase, release 14.0. http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk . (September 2009)
-
- Shan ZX, Lin QX, Fu YH, Deng CY, Zhou ZL, Zhu JN, Liu XY, Zhang YY, Li Y, Lin SG, Yu XY. Upregulated expression of miR-1/miR-206 in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;381:597–601. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.097. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Thatcher JE, DiMaio JM, Naseem RH, Marshall WS, Hill JA, Olson EN. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:13027–13032. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805038105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dong S, Cheng Y, Yang J, Li J, Liu X, Wang X, Wang D, Krall TJ, Delphin ES, Zhang C. MicroRNA expression signature and the role of microRNA-21 in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:29514–29525. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.027896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

