Connective tissue growth factor is required for skeletal development and postnatal skeletal homeostasis in male mice
- PMID: 20534727
- PMCID: PMC2940511
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0145
Connective tissue growth factor is required for skeletal development and postnatal skeletal homeostasis in male mice
Abstract
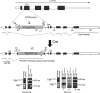
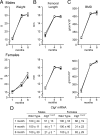
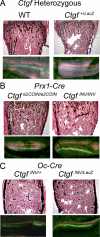
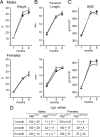
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), a member of the cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr 61), CTGF, nephroblastoma overexpressed (NOV) (CCN) family of proteins, is synthesized by osteoblasts, and its overexpression inhibits osteoblastogenesis and causes osteopenia. The global inactivation of Ctgf leads to defective endochondral bone formation and perinatal lethality; therefore, the consequences of Ctgf inactivation on the postnatal skeleton are not known. To study the function of CTGF, we generated Ctgf(+/LacZ) heterozygous null mice and tissue-specific null Ctgf mice by mating Ctgf conditional mice, where Ctgf is flanked by lox sequences with mice expressing the Cre recombinase under the control of the paired-related homeobox gene 1 (Prx1) enhancer (Prx1-Cre) or the osteocalcin promoter (Oc-Cre). Ctgf(+/LacZ) heterozygous mice exhibited transient osteopenia at 1 month of age secondary to decreased trabecular number. A similar osteopenic phenotype was observed in 1-month-old Ctgf conditional null male mice generated with Prx1-Cre, suggesting that the decreased trabecular number was secondary to impaired endochondral bone formation. In contrast, when the conditional deletion of Ctgf was achieved by Oc-Cre, an osteopenic phenotype was observed only in 6-month-old male mice. Osteoblast and osteoclast number, bone formation, and eroded surface were not affected in Ctgf heterozygous or conditional null mice. In conclusion, CTGF is necessary for normal skeletal development but to a lesser extent for postnatal skeletal homeostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Brigstock DR 2003 The CCN family: a new stimulus package. J Endocrinol 178:169–175 - PubMed
-
- Garcia Abreu J, Coffinier C, Larraín J, Oelgeschläger M, De Robertis EM 2002 Chordin-like CR domains and the regulation of evolutionarily conserved extracellular signaling systems. Gene 287:39–47 - PubMed
-
- Luo Q, Kang Q, Si W, Jiang W, Park JK, Peng Y, Li X, Luu HH, Luo J, Montag AG, Haydon RC, He TC 2004 Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) is regulated by Wnt and bone morphogenetic proteins signaling in osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem 279:55958–55968 - PubMed
-
- Parisi MS, Gazzerro E, Rydziel S, Canalis E 2006 Expression and regulation of CCN genes in murine osteoblasts. Bone 38:671–677 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

