Acute disruption of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1 in the honeybee brain selectively impairs memory formation
- PMID: 20534830
- PMCID: PMC6632693
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5543-09.2010
Acute disruption of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1 in the honeybee brain selectively impairs memory formation
Abstract
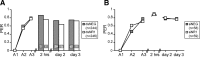
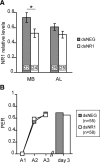
Memory formation is a continuous process composed of multiple phases that can develop independently from each other. These phases depend on signaling pathways initiated after the activation of receptors in different brain regions. The NMDA receptor acts as a sensor of coincident activity between neural inputs, and, as such, its activation during learning is thought to be crucial for various forms of memory. In this study, we inhibited the expression of the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor in the honeybee brain using RNA interference. We show that the disruption of the subunit expression in the mushroom body region of the honeybee brain during and shortly after appetitive learning selectively impaired memory. Although the formation of mid-term memory and early long-term memory was impaired, late long-term memory was left intact. This indicates that late long-term memory formation differs in its dependence on NMDA receptor activity from earlier memory phases.
Figures
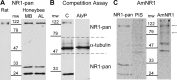
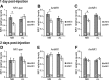

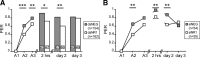
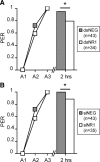
Comment in
-
What's the buzz about honeybee memory?J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 3;30(44):14593-4. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3951-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21048116 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barbara GS, Zube C, Rybak J, Gauthier M, Grunewald B. Acetylcholine, GABA and glutamate induce ionic currents in cultured antennal lobe neurons of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2005;191:823–836. - PubMed
-
- Bitterman ME, Menzel R, Fietz A, Schafer S. Classical conditioning of proboscis extension in honeybees (Apis mellifera) J Comp Psychol. 1983;97:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Breer H, Sattelle DB. Molecular properties and functions of insect acetylcholine receptors. J Insect Physiol. 1987;33:771–790.
-
- Casadio A, Martin KC, Giustetto M, Zhu H, Chen M, Bartsch D, Bailey CH, Kandel ER. A transient, neuron-wide form of CREB-mediated long-term facilitation can be stabilized at specific synapses by local protein synthesis. Cell. 1999;99:221–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
