Afferent-specific AMPA receptor subunit composition and regulation of synaptic plasticity in midbrain dopamine neurons by abused drugs
- PMID: 20534838
- PMCID: PMC2900154
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1507-10.2010
Afferent-specific AMPA receptor subunit composition and regulation of synaptic plasticity in midbrain dopamine neurons by abused drugs
Abstract
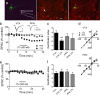
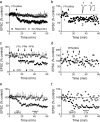
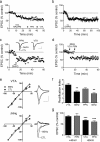
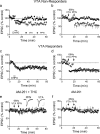
Ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine (DA) neurons play a pivotal role in processing reward-related information and are involved in drug addiction and mental illness in humans. Information is conveyed to the VTA in large part by glutamatergic afferents that arise in various brain nuclei, including the pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN). Using a unique rat brain slice preparation, we found that PPN stimulation activates afferents targeting GluR2-containing AMPA receptors (AMPAR) on VTA DA neurons, and these afferents did not exhibit long-term depression (LTD). In contrast, activation of glutamate afferents onto the same DA neurons via stimulation within the VTA evoked EPSCs mediated by GluR2-lacking AMPARs that demonstrated LTD or EPSCs mediated by GluR2-containing AMPA receptors that did not express LTD. Twenty-four hours after single cocaine injections to rats, GluR2-lacking AMPARs were increased at both PPN and local VTA projections, and this permitted LTD expression in both pathways. Single injections with the main psychoactive ingredient of marijuana, Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(9)-THC), increased GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors and permitted LTD in only the PPN pathway, and these effects were prevented by in vivo pretreatment with the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251. These results demonstrate that cocaine more globally increases GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors at all glutamate synapses on VTA dopamine neurons, whereas Delta(9)-THC selectively increased GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors at subcortical PPN synapses. This suggests that different abused drugs may exert influence over distinct sets of glutamatergic afferents to VTA DA neurons which may be associated with different reinforcing or addictive properties of these drugs.
Figures

References
-
- Bellone C, Lüscher C. mGluRs induce a long-term depression in the ventral tegmental area that involves a switch of the subunit composition of AMPA receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:1280–1288. - PubMed
-
- Bellone C, Lüscher C. Cocaine triggered AMPA receptor redistribution is reversed in vivo by mGluR-dependent long-term depression. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:636–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
