Gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep disorders: evidence for a causal link and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 20535322
- PMCID: PMC2879818
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2010.16.1.22
Gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep disorders: evidence for a causal link and therapeutic implications
Abstract
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and sleep disturbances are both common health problems. There is a significant association between disturbed sleep and GERD, and this may be bidirectional. Sleep disorders may induce gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances, while GI symptoms also may provoke or worsen sleep derangements. Reflux of gastric acid is a less frequent event during sleep, however, acid clearance mechanisms (including swallowing, salivation and primary esophageal motility) are impaired during sleep resulting in prolongation of acid contact time. Nighttime reflux can lead to sleep disturbance and sleep disturbance may further aggravate GERD by prolonged acid contact time and heightened sensory perception. This may facilitate the occurrence of complicated GERD and decreased quality of life. However, the interplay between sleep problems and GERD is complex, and there are still relatively limited data on this issue. Further investigation of sleep-related GERD may identify common pathophysiological themes and new therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures
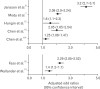

References
-
- Locke GR, 3rd, Zinsmeister AR, Fett SL, Melton LJ, 3rd, Talley NJ. Overlap of gastrointestinal symptom complexes in a US community. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005;17:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, et al. U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:1569–1580. - PubMed
-
- Roth T, Roehrs T. Insomnia: epidemiology, characteristics, and consequences. Clin Cornerstone. 2003;5:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Taylor DJ, Mallory LJ, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH, Riedel BW, Bush AJ. Comorbidity of chronic insomnia with medical problems. Sleep. 2007;30:213–218. - PubMed
-
- Roth T. Comorbid insomnia: current directions and future challenges. Am J Manag Care. 2009;15(Suppl):S6–S13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

