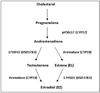
Hormonal influences on cognition and risk for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20535591
- PMCID: PMC3058507
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-010-0122-6
Hormonal influences on cognition and risk for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Research increasingly suggests that changes in estrogen levels during aging may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease, the most common type of dementia. This update reviews the newest information about estrogen and cognitive aging, including information regarding the role of bioavailable estrogen in older women and men, use of selective estrogen receptor modulators to improve cognition, and studies of genetic risk factors to elucidate the effects of endogenous estrogen on aging and cognition. Future trials are needed to determine whether alternate timing, dosage, formulation, or method of administration of hormone replacement can reduce the risk of dementia.
Figures
References
-
- Goodman Y, Bruce AJ, Cheng B, Mattson MP. Estrogens attenuate and corticosterone exacerbates excitotoxicity, oxidative injury, and amyloid beta-peptide toxicity in hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem. 1996;66:1836–1844. - PubMed
-
- Luine VN. Estradiol increases choline acetyltransferase activity in specific basal forebrain nuclei and projection areas of female rats. Exp Neurol. 1985;89:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Behl C, Widmann M, Trapp T, Holsboer F. 17-beta estradiol protects neurons from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;216:473–482. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe AB, Toran-Allerand CD, Greengard P, Gandy SE. Estrogen regulates metabolism of Alzheimer amyloid beta precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13065–13068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 HD079123/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG07232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 MH2004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG014673/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG028786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG007370/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG023749/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01HD035897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020048/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG034189/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD035897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG036040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034189/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG007232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA125461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG007370/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG08702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG014673/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical