Reconstruction of the orientation distribution function in single- and multiple-shell q-ball imaging within constant solid angle
- PMID: 20535807
- PMCID: PMC2911516
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22365
Reconstruction of the orientation distribution function in single- and multiple-shell q-ball imaging within constant solid angle
Abstract
q-Ball imaging is a high-angular-resolution diffusion imaging technique that has been proven very successful in resolving multiple intravoxel fiber orientations in MR images. The standard computation of the orientation distribution function (the probability of diffusion in a given direction) from q-ball data uses linear radial projection, neglecting the change in the volume element along each direction. This results in spherical distributions that are different from the true orientation distribution functions. For instance, they are neither normalized nor as sharp as expected and generally require postprocessing, such as artificial sharpening. In this paper, a new technique is proposed that, by considering the solid angle factor, uses the mathematically correct definition of the orientation distribution function and results in a dimensionless and normalized orientation distribution function expression. Our model is flexible enough so that orientation distribution functions can be estimated either from single q-shell datasets or by exploiting the greater information available from multiple q-shell acquisitions. We show that the latter can be achieved by using a more accurate multiexponential model for the diffusion signal. The improved performance of the proposed method is demonstrated on artificial examples and high-angular-resolution diffusion imaging data acquired on a 7-T magnet.
Figures


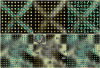
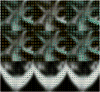
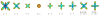
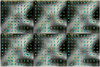
References
-
- Wedeen VJ, Hagmann P, Tseng WI, Reese TG, Weisskoff RM. Mapping complex tissue architecture with diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2005;54(6):1377–1386. - PubMed
-
- Tuch DS, Reese TG, Wiegell MR, Makris N, Belliveau JW, Wedeen VJ. High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;48(4):577–582. - PubMed
-
- Tuch DS. Q-ball imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2004;52(6):1358–1372. - PubMed
-
- Funk P. Über eine geometrische Anwendung der Abelschen Integralgleichung. Mathematische Annalen. 1916;77:129–135.
-
- Anderson AW. Measurement of fiber orientation distributions using high angular resolution diffusion imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2005;54(5):1194–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

