Macrocyclic inhibitors of hsp90
- PMID: 20536417
- PMCID: PMC3105290
- DOI: 10.2174/156802610792232088
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hsp90
Abstract
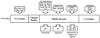
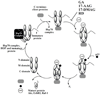
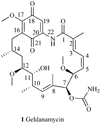
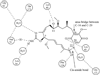
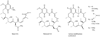
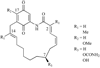
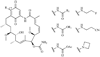
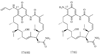
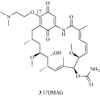
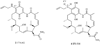
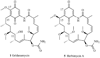
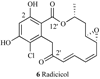
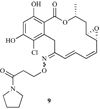
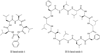
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a family of highly conserved proteins, whose expression increases in response to stresses that may threaten cell survival. Over the past decade, heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for cancer as it plays a vital role in normal cell maturation and acts as a molecular chaperone for proper folding, assembly, and stabilization of many oncogenic proteins. To date, a majority of Hsp90 inhibitors that have been discovered are macrocycles. The relatively rigid conformation provided by the macrocyclic scaffold allows for a selective interaction with a biological target such as Hsp90. This review highlights the discovery and development of nine macrocycles that inhibit the function of Hsp90, detailing their potency and the client proteins affected by Hsp90 inhibition.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Drug-mediated targeted disruption of multiple protein activities through functional inhibition of the Hsp90 chaperone complex.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(29):3122-38. doi: 10.2174/092986707782793925. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 18220746 Review.
-
Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibitors: An Update on Achievements, Challenges, and Future Directions.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 12;63(5):1798-1822. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00940. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31663736 Review.
-
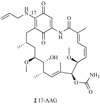
Heat-shock protein 90 inhibitors in cancer therapy: 17AAG and beyond.Future Oncol. 2005 Apr;1(2):273-81. doi: 10.1517/14796694.1.2.273. Future Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16555999 Review.
-
HSP90 inhibitors: multi-targeted antitumor effects and novel combinatorial therapeutic approaches in cancer therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(24):3081-92. doi: 10.2174/092986709788802999. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19689285 Review.
-
Spotlight on 17-AAG as an Hsp90 inhibitor for molecular targeted cancer treatment.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019 May;93(5):760-786. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13486. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019. PMID: 30697932 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulphoxythiocarbamates modify cysteine residues in HSP90 causing degradation of client proteins and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation.Br J Cancer. 2014 Jan 7;110(1):71-82. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.710. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24322890 Free PMC article.
-
FDA-approved drugs featuring macrocycles or medium-sized rings.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 Jan;358(1):e2400890. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202400890. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 39865335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel starting points for fragment-based drug design against human heat-shock protein 90 identified using crystallographic fragment screening.IUCrJ. 2025 Mar 1;12(Pt 2):177-187. doi: 10.1107/S2052252524012247. IUCrJ. 2025. PMID: 39819741 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of Hsp90 inhibitors: exploring the SAR of Sansalvamide A derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Sep 15;18(18):6822-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.07.042. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20708938 Free PMC article.
-
Macrocycles that inhibit the binding between heat shock protein 90 and TPR-containing proteins.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Dec 16;6(12):1357-66. doi: 10.1021/cb200203m. Epub 2011 Oct 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21950602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morimoto RI, Kline MP, Bimston DN, Cotto JJ. The heat-shock response: regulation and function of heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones. Essays Biochem. 1997;32:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol:from nascent chain to folded protein. Science. 2002;295:1852–1858. - PubMed
-
- Parsell DA, Lindquist S. The function of heat-shock proteins in stress tolerance: degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1993;27:437–496. - PubMed
-
- Welch WJ, Feramisco JR. Purification of the major mammalian heat shock proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257(24):14949–14959. - PubMed
-
- Crevel G, Bates H, Huikeshoven H, Cotterill S. The Drosophila Dpit47 protein is a nuclear Hsp90 co-chaperone that interacts with DNA polymerase alpha. J. Cell Sci. 2001;114(Pt 11):2015–2025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

