HLA-DR-restricted T-cell responses to factor VIII epitopes in a mild haemophilia A family with missense substitution A2201P
- PMID: 20536985
- PMCID: PMC2885051
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2516.2008.01905.x
HLA-DR-restricted T-cell responses to factor VIII epitopes in a mild haemophilia A family with missense substitution A2201P
Abstract
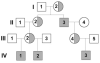
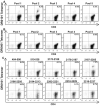
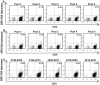
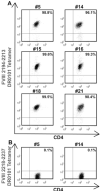
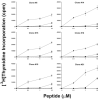
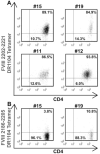
An HLA-DRA-DRB1*0101-restricted T-cell epitope in the factor VIII (FVIII) C2 domain occurred in a mild haemophilia A patient with missense substitution FVIII-A2201P. His T cells responded to synthetic peptides FVIII(2186-2205) and FVIII(2194-2213) (J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: 2399). T cells from family members with genotype FVIII-A2201P were analysed to determine if FVIII-specific T cells occur in individuals with a haemophilic mutation but no clinically significant inhibitor response. Fluorescent MHC class II tetramers corresponding to subjects'HLA-DRB1 types were loaded with 20-mer peptides and utilized to label antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. T-cell responses to peptides spanning the FVIII-C2 sequence were evaluated. T cells recognizing specific peptides were cloned, and antigen specificity was verified by proliferation assays. Plasma and/or purified IgG samples were tested for FVIII inhibitory activity. CD4+ T cells and T-cell clones from two brothers who shared the DRB1*0101 allele responded to FVIII(2194-2213). A haemophilic cousin's HLA-DRA-DRB1*1104-restricted response to FVIII(2202-2221) was detected only when CD4+CD25+ cells were depleted. A great uncle and two obligate carriers had no detectable FVIII-C2-specific T cells. Concentrated IgG from the brother without a clinical inhibitor response showed a low-titre FVIII inhibitor. FVIII-specific T cells and inhibitory IgG were found in a previously infused, haemophilic subject who had a sub-clinical FVIII inhibitor. CD4+CD25+ depleted T cells from a non-infused haemophilic cousin recognized an overlapping FVIII epitope, indicating a latent HLA-DRA-DRB1*1104-restricted T-cell response to FVIII. Specific T-cell responses to FVIII can occur without clinically significant inhibitors.
Figures
References
-
- Hoyer LW. Hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenfort S, Kreuz W, Scharrer I, Linde R, Funk M, Gungor T, et al. Incidence of development of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in haemophiliacs. Lancet. 1992;339:594–8. - PubMed
-
- Lusher JM, Arkin S, Abildgaard CF, Schwartz RS, The Kogenate Previously Untreated Patient Study Group Recombinant Factor VIII for the treatment of previously untreated patients with hemophilia A — safety, efficacy, and development of inhibitor. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:453–9. - PubMed
-
- Darby SC, Keeling DM, Spooner RJ, Kan SW, Giangrande PL, Collins PW, et al. The incidence of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in the hemophilia population of the UK and their effect on subsequent mortality, 1977-99. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1047–54. - PubMed
-
- Thompson AR, Murphy ME, Liu ML, Saenko EL, Healey JF, Lollar P, et al. Loss of tolerance to exogenous and endogenous factor VIII in a mild hemophilia A patient with an Arg 593 to Cys mutation. Blood. 1997;90:1902–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

