Risk factors for radiographic progression in psoriatic arthritis: subanalysis of the randomized controlled trial ADEPT
- PMID: 20537151
- PMCID: PMC2911906
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3049
Risk factors for radiographic progression in psoriatic arthritis: subanalysis of the randomized controlled trial ADEPT
Abstract
Introduction: To identify independent predictors of radiographic progression in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) for patients treated with adalimumab or placebo in the Adalimumab Effectiveness in PsA Trial (ADEPT).
Methods: Univariate analyses and multivariate linear regression analyses assessed risk for radiographic progression (change in modified total Sharp score, DeltamTSS>0.5) from baseline to week 24 for C-reactive protein (CRP) and other baseline variables, and for 24-week time-averaged CRP (univariate analysis only). Subanalyses determined mean DeltamTSS for CRP subgroups. Analyses were post hoc, with observed data.
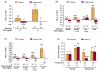
Results: One hundred and forty-four adalimumab-treated patients and 152 placebo-treated patients were assessed. Mean CRP was 64% lower by week 2 with adalimumab and essentially unchanged with placebo. Univariate analyses indicated that elevated CRP at baseline and time-averaged CRP were strongly associated with radiographic progression for placebo-treated patients but not for adalimumab-treated patients. Multivariate analysis confirmed that elevated baseline CRP was the only strong independent risk factor for radiographic progression (for CRP>or=1.0 mg/dl: odds ratio=3.28, 95% confidence interval=1.66 to 6.51, P<0.001). Adalimumab treatment reduced risk of progression approximately fivefold. The difference between mean DeltamTSS for adalimumab versus placebo was greatest for patients with baseline CRP>or=2.0 mg/dl (-0.5 vs. 2.6).
Conclusions: Systemic inflammation in PsA, as indicated by elevated baseline CRP, was the only strong independent predictor of radiographic progression. This association was observed predominantly for placebo-treated patients. Adalimumab treatment substantially reduced the overall risk of radiographic progression, and provided greatest radiographic benefit for patients with the greatest CRP concentrations at baseline.
Trial registration: Trial registration: NCT00195689.
Figures

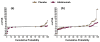
References
-
- Gladman DD. In: Psoriatic Arthritis and Reactive Arthritis. Ritchlin CT, Fitzgerald O, editor. St Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier; 2007. Psoriatic arthritis clinical features; pp. 9–18.
-
- Gladman DD, Shuckett R, Russell ML, Thorne JC, Schachter RK. Psoriatic arthritis (PSA): an analysis of 220 patients. Q J Med. 1987;62:127–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

