The differential regulation of cell motile activity through matrix stiffness and porosity in three dimensional collagen matrices
- PMID: 20537378
- PMCID: PMC2900504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.04.064
The differential regulation of cell motile activity through matrix stiffness and porosity in three dimensional collagen matrices
Abstract
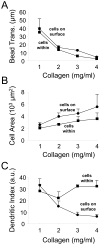
In three dimensional collagen matrices, cell motile activity results in collagen translocation, cell spreading and cell migration. Cells can penetrate into the matrix as well as spread and migrate along its surface. In the current studies, we quantitatively characterize collagen translocation, cell spreading and cell migration in relationship to collagen matrix stiffness and porosity. Collagen matrices prepared with 1-4 mg/ml collagen exhibited matrix stiffness (storage modulus measured by oscillating rheometry) increasing from 4 to 60 Pa and matrix porosity (measured by scanning electron microscopy) decreasing from 4 to 1 microm(2). Over this collagen concentration range, the consequences of cell motile activity changed markedly. As collagen concentration increased, cells no longer were able to cause translocation of collagen fibrils. Cell migration increased and cell spreading changed from dendritic to more flattened and polarized morphology depending on location of cells within or on the surface of the matrix. Collagen translocation appeared to depend primarily on matrix stiffness, whereas cell spreading and migration were less dependent on matrix stiffness and more dependent on collagen matrix porosity.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Pedersen JA, Boschetti F, Swartz MA. Effects of extracellular fiber architecture on cell membrane shear stress in a 3D fibrous matrix. J Biomech. 2007;40:1484–92. - PubMed
-
- Langevin HM, Bouffard NA, Badger GJ, Iatridis JC, Howe AK. Dynamic fibroblast cytoskeletal response to subcutaneous tissue stretch ex vivo and in vivo. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288:C747–56. - PubMed
-
- Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:349–63. - PubMed
-
- Grinnell F. Fibroblast biology in three-dimensional collagen matrices. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:264–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

