Lineage programming: navigating through transient regulatory states via binary decisions
- PMID: 20537527
- PMCID: PMC2944227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.04.010
Lineage programming: navigating through transient regulatory states via binary decisions
Abstract
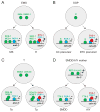
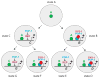
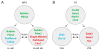
Lineage-based mechanisms are widely used to generate cell type diversity in both vertebrates and invertebrates. For the past few decades, the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has served as a primary model system to study this process because of its fixed and well-characterized cell lineage. Recent studies conducted at the level of single cells and individual cis-regulatory elements suggest a general model by which cellular diversity is generated in this organism. During its developmental history a cell passes through multiple transient regulatory states characterized by the expression of specific sets of transcription factors. The transition from one state to another is driven by a general binary decision mechanism acting at each successive division in a reiterative manner and ending up with the activation of the terminal differentiation program upon terminal division. A similar cell fate specification system seems to play a role in generating cellular diversity in the nervous system of more complex organisms such as Drosophila and vertebrates.
Figures
References
-
- Sawa H. Specification of neurons through asymmetric cell divisions. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20:44–49. - PubMed
-
- Sulston JE, Schierenberg E, White JG, Thomson JN. The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1983;100:64–119. - PubMed
-
- Maduro MF, Rothman JH. Making worm guts: the gene regulatory network of the Caenorhabditis elegans endoderm. Dev Biol. 2002;246:68–85. - PubMed
-
- Baugh LR, Hill AA, Slonim DK, Brown EL, Hunter CP. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development. 2003;130:889–900. - PubMed
-
- Murray JI, Bao Z, Boyle TJ, Boeck ME, Mericle BL, Nicholas TJ, Zhao Z, Sandel MJ, Waterston RH. Automated analysis of embryonic gene expression with cellular resolution in C. elegans. Nat Methods. 2008;5:703–709. - PMC - PubMed
-
This article describes an automated method to determine the expression pattern of fluorescent reporters during embryonic development with single cell resolution
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

