Robust growth of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20537537
- PMCID: PMC2902570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.045
Robust growth of Escherichia coli
Abstract
The quantitative study of the cell growth has led to many fundamental insights in our understanding of a wide range of subjects, from the cell cycle to senescence. Of particular importance is the growth rate, whose constancy represents a physiological steady state of an organism. Recent studies, however, suggest that the rate of elongation during exponential growth of bacterial cells decreases cumulatively with replicative age for both asymmetrically and symmetrically dividing organisms, implying that a "steady-state" population consists of individual cells that are never in a steady state of growth. To resolve this seeming paradoxical observation, we studied the long-term growth and division patterns of Escherichia coli cells by employing a microfluidic device designed to follow steady-state growth and division of a large number of cells at a defined reproductive age. Our analysis of approximately 10(5) individual cells reveals a remarkable stability of growth whereby the mother cell inherits the same pole for hundreds of generations. We further show that death of E. coli is not purely stochastic but is the result of accumulating damages. We conclude that E. coli, unlike all other aging model systems studied to date, has a robust mechanism of growth that is decoupled from cell death.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
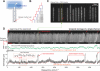

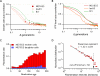

Comment in
-
Synthetic biology: Precision timing in a cell.Nature. 2016 Oct 27;538(7626):462-463. doi: 10.1038/nature19478. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27732579 No abstract available.
References
-
- Monod J. The growth of bacterial cultures. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1949;3:371–394.
-
- Schaechter M, Maaloe O, Kjeldgaard NO. Dependency on Medium and Temperature of Cell Size and Chemical Composition during Balanced Growth of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958;19(3):592–606. - PubMed
-
- Kjeldgaard NO, Maaloe O, Schaechter M. The transition between different physiological states during balanced growth of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958;19(3):607–616. - PubMed
-
- Helmstetter C, Cooper S. DNA synthesis during the division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J. Mol. Biol. 1968;31:507–518. - PubMed
-
- Donachie WD. Relationship between cell size and time of initiation of DNA replication. Nature. 1968;219:1077–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

