A placebo-controlled trial of memantine for cocaine dependence with high-value voucher incentives during a pre-randomization lead-in period
- PMID: 20537812
- PMCID: PMC2930076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.04.006
A placebo-controlled trial of memantine for cocaine dependence with high-value voucher incentives during a pre-randomization lead-in period
Abstract
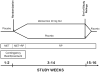
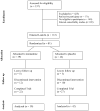
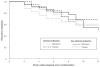
Preclinical findings suggest that the inhibition of NMDA glutamatergic neurotransmission may have beneficial effects in the treatment of cocaine dependence. We hypothesized that memantine, a low potency, uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, would be safe and effective in the treatment of cocaine dependence, particularly in preventing relapse to cocaine use in abstinent individuals. Cocaine dependent patients (N=112) were enrolled. The trial began with a 2-week placebo lead-in period during which patients received high-value voucher contingency management to induce abstinence. Participants were then randomized to receive either memantine 20mg bid (N=39) or placebo (N=42) for 12-weeks in combination with individual relapse-prevention therapy. The randomization was stratified by abstinence status during the lead-in period. The primary outcome was the weekly proportion of days of cocaine use. There were no significant differences in cocaine use outcome between the groups treated with memantine versus placebo. Thus, the efficacy of memantine 40 mg/d for the treatment of cocaine dependence was not supported. Urine-confirmed abstinence during the lead-in period was achieved by 44% of participants, and was a strong predictor of subsequent cocaine abstinence during the trial. This suggests that this clinical trial design, an intensive behavioral intervention during a lead-in period, resolves cocaine dependent patients into two subgroups, one that rapidly achieves sustained abstinence and may not need a medication, and another that displays persistent cocaine use and would most likely benefit from a medication to help induce abstinence. Targeting the latter subgroup may advance medication development efforts.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alterman AI, Kampman K, Boardman CR, Cacciola JS, Rutherford MJ, McKay JR, Maany I. A cocaine-positive baseline urine predicts outpatient treatment attrition and failure to attain initial abstinence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1997;46:79–85. - PubMed
-
- Bespalov AY, Dravolina OA, Zvartau EE, Beardsley PM, Balster RL. Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on cocaine-conditioned motor activity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000a;390:303–311. - PubMed
-
- Bespalov AY, Zvartau EE, Balster RL, Beardsley PM. Effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior by priming injections of cocaine or exposures to cocaine-associated cues in rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2000b;11:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Bisaga A, Aharonovich E, Garawi F, Levin FR, Rubin E, Raby WN, Nunes EV. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of gabapentin for cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;81:267–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

