Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and antiviral activity of 3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine and its prodrugs
- PMID: 20538384
- PMCID: PMC7127469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.05.028
Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and antiviral activity of 3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine and its prodrugs
Abstract
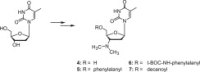
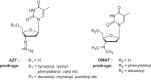
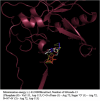
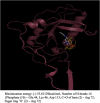
A probable NRTI molecule, viz. 3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (4) and its 5'-O-carboxyl ester prodrugs - 5'-(N-alpha-BOC-L-phenylalanyl)-3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (5), 5'-L-phenylalanyl-3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (6) and 5'-decanoyl-3'-N,N-dimethylamino-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (7) have been synthesized and screened against HIV, HSV-1 and 2, parainfluenza-3, vesicular stomatitis and several other viruses. The compound 6 showed good antiviral activity with EC(50) value 0.03 microM (SI=8) against VSV in Hela and HEL cell lines. However, the lead compound 4 and its derivatives 5, 6 and 7 showed no remarkable activity against HIV-1 and other viruses. Molecular docking studies with HIV-1 RT using DS 2.5 and pymol softwares have shown marked differences in the interaction patterns between the lead compound 4 and AZT.
2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thymidine analogs as potential antiviral agents.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2008;(52):263-4. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrn133. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2008. PMID: 18776354
-
Diastereoselective synthesis of aryloxy phosphoramidate prodrugs of 3'-deoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine monophosphate.J Med Chem. 2010 Nov 11;53(21):7675-81. doi: 10.1021/jm100817f. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20945915
-
In vitro anti-hepatitis B virus activities of 5"-O-myristoyl analogue derivatives of 3"-fluoro-2",3"-dideoxythymidine (FLT) and 3"-azido-2",3"-dideoxythymidine (AZT).J Pharm Pharm Sci. 1998 Sep-Dec;1(3):108-14. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 1998. PMID: 10948398
-
Novel approaches for designing 5'-O-ester prodrugs of 3'-azido-2', 3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT).Curr Med Chem. 2000 Oct;7(10):995-1039. doi: 10.2174/0929867003374372. Curr Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 10911016 Review.
-
"Lock-in"-cycloSal-pronucleotides - a new generation of chemical Trojan Horses?Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004 May;4(4):383-94. doi: 10.2174/1389557043403972. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15134541 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Pharmacokinetics, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of Nucleoside Analogs for Drug Discovery- A Mini Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(11):1070-1088. doi: 10.2174/0113895575258033231024073521. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37957918 Review.
-
Drug Discovery and Exploration of Heterocycles for the Development of Anti-HIV Agents.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(3):e18715265290911. doi: 10.2174/0118715265290911240611072422. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39185647 Review.
References
-
- Ali H., Ahmed N., Tessier G., Lier J.E.V. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;15:317–319. - PubMed
-
- Genini D., Adachi S., Chao Q., Rose D.W., Carrera C.J., Kottam H.B., Carson D., Leoni L.M. Blood. 2000;96:3537–3543. - PubMed
-
- Gudumundsson K.S., Freeman G.A., Drach J.C., Townsend L.B. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:2473–2478. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y.S., Kim B.H. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002;20:1395–1397. - PubMed
-
- Galmarini C.M., Mackey J.R., Dumontet C. Nature. 2001;15:875–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

