TGF-beta and immune cells: an important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression
- PMID: 20538542
- PMCID: PMC2891151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2010.04.002
TGF-beta and immune cells: an important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression
Abstract
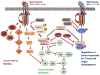
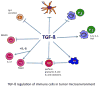
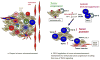
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) plays an important role in tumor initiation and progression, functioning as both a suppressor and a promoter. The mechanisms underlying this dual role of TGF-beta remain unclear. TGF-beta exerts systemic immune suppression and inhibits host immunosurveillance. Neutralizing TGF-beta enhances CD8+ T-cell- and NK-cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses. It also increases neutrophil-attracting chemokines resulting in recruitment and activation of neutrophils with an antitumor phenotype. In addition to its systemic effects, TGF-beta regulates infiltration of inflammatory/immune cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment causing direct changes in tumor cells. Understanding TGF-beta regulation at the interface of tumor and host immunity should provide insights into developing effective TGF-beta antagonists and biomarkers for patient selection and efficacy of TGF-beta antagonist treatment.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Bierie B, Moses HL. Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6 (7):506–520. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature. 2003;425 (6958):577–584. - PubMed
-
- Nakao A, et al. Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature. 1997;389 (6651):631–635. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi H, et al. The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell. 1997;89 (7):1165–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

