Head of myosin IX binds calmodulin and moves processively toward the plus-end of actin filaments
- PMID: 20538589
- PMCID: PMC2915729
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101105
Head of myosin IX binds calmodulin and moves processively toward the plus-end of actin filaments
Abstract
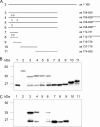
Mammalian myosin IXb (Myo9b) has been shown to exhibit unique motor properties in that it is a single-headed processive motor and the rate-limiting step in its chemical cycle is ATP hydrolysis. Furthermore, it has been reported to move toward the minus- and the plus-end of actin filaments. To analyze the contribution of the light chain-binding domain to the movement, processivity, and directionality of a single-headed processive myosin, we expressed constructs of Caenorhabditis elegans myosin IX (Myo9) containing either the head (Myo9-head) or the head and the light chain-binding domain (Myo9-head-4IQ). Both constructs supported actin filament gliding and moved toward the plus-end of actin filaments. We identified in the head of class IX myosins a calmodulin-binding site at the N terminus of loop 2 that is unique among the myosin superfamily members. Ca(2+)/calmodulin negatively regulated ATPase and motility of the Myo9-head. The Myo9-head demonstrated characteristics of a processive motor in that it supported actin filament gliding and pivoting at low motor densities. Quantum dot-labeled Myo9-head moved along actin filaments with a considerable run length and frequently paused without dissociating even in the presence of obstacles. We conclude that class IX myosins are plus-end-directed motors and that even a single head exhibits characteristics of a processive motor.
Figures


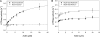



Similar articles
-
A unique ATP hydrolysis mechanism of single-headed processive myosin, myosin IX.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 24;281(8):4949-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509141200. Epub 2005 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16338935
-
Myosin IXb is a single-headed minus-end-directed processive motor.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;4(4):302-6. doi: 10.1038/ncb774. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11901422
-
The loop2 insertion of type IX myosin acts as an electrostatic actin tether that permits processive movement.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 9;9(1):e84874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084874. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416302 Free PMC article.
-
Class IX Myosins: Motorized RhoGAP Signaling Molecules.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1239:381-389. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38062-5_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32451867 Review.
-
The chemical mechanism of myosin-I: implications for actin-based motility and the evolution of the myosin family of motor proteins.Cell Struct Funct. 1996 Oct;21(5):351-6. doi: 10.1247/csf.21.351. Cell Struct Funct. 1996. PMID: 9118240 Review.
Cited by
-
The RhoGAP HUM-7/Myo9 integrates signals to modulate RHO-1/RhoA during embryonic morphogenesis in Caenorhabditiselegans.Development. 2018 Dec 3;145(23):dev168724. doi: 10.1242/dev.168724. Development. 2018. PMID: 30389847 Free PMC article.
-
Myo9b is a key player in SLIT/ROBO-mediated lung tumor suppression.J Clin Invest. 2015 Nov 3;125(12):4407-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI81673. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26529257 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mutations in the MYO9A gene in patients with congenital myasthenic syndrome.Brain. 2016 Aug;139(Pt 8):2143-53. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww130. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Brain. 2016. PMID: 27259756 Free PMC article.
-
Myosins in cell junctions.Bioarchitecture. 2012 Sep-Oct;2(5):158-70. doi: 10.4161/bioa.21791. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Bioarchitecture. 2012. PMID: 22954512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of collective cell migration by RhoGAP myosin IXA.Small GTPases. 2012 Oct-Dec;3(4):213-8. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.20495. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22735295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bähler M. (2000) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1496, 52–59 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

