Pgrmc1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) associates with epidermal growth factor receptor and regulates erlotinib sensitivity
- PMID: 20538600
- PMCID: PMC2915713
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134585
Pgrmc1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) associates with epidermal growth factor receptor and regulates erlotinib sensitivity
Abstract
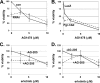
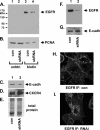
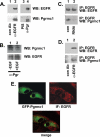
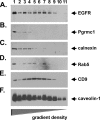
Tumorigenesis requires the concerted action of multiple pathways, including pathways that stimulate proliferation and metabolism. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a transmembrane receptor-tyrosine kinase that is associated with cancer progression, and the EGFR inhibitors erlotinib/tarceva and tyrphostin/AG-1478 are potent anti-cancer therapeutics. Pgrmc1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) is a cytochrome b(5)-related protein that is up-regulated in tumors and promotes cancer growth. Pgrmc1 and its homologues have been implicated in cell signaling, and we show here that Pgrmc1 increases susceptibility to AG-1478 and erlotinib, increases plasma membrane EGFR levels, and co-precipitates with EGFR. Pgrmc1 co-localizes with EGFR in cytoplasmic vesicles and co-fractionates with EGFR in high density microsomes. The findings have therapeutic potential because a Pgrmc1 small molecule ligand, which inhibits growth in a variety of cancer cell types, de-stabilized EGFR in multiple tumor cell lines. EGFR is one of the most potent receptor-tyrosine kinases driving tumorigenesis, and our data support a role for Pgrmc1 in promoting several cancer phenotypes at least in part by binding EGFR and stabilizing plasma membrane pools of the receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Ritter C. A., Arteaga C. L. (2003) Semin. Oncol. 30, 3–11 - PubMed
-
- Salomon D. S., Brandt R., Ciardiello F., Normanno N. (1995) Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 19, 183–232 - PubMed
-
- Ono M., Kuwano M. (2006) Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 7242–7251 - PubMed
-
- Bareschino M. A., Schettino C., Troiani T., Martinelli E., Morgillo F., Ciardiello F. (2007) Ann. Oncol. 18, vi35–41 - PubMed
-
- Lynch T. J., Bell D. W., Sordella R., Gurubhagavatula S., Okimoto R. A., Brannigan B. W., Harris P. L., Haserlat S. M., Supko J. G., Haluska F. G., Louis D. N., Christiani D. C., Settleman J., Haber D. A. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2129–2139 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

