In silico docking and electrophysiological characterization of lacosamide binding sites on collapsin response mediator protein-2 identifies a pocket important in modulating sodium channel slow inactivation
- PMID: 20538611
- PMCID: PMC2919092
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128801
In silico docking and electrophysiological characterization of lacosamide binding sites on collapsin response mediator protein-2 identifies a pocket important in modulating sodium channel slow inactivation
Abstract
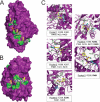
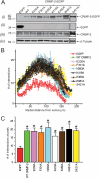
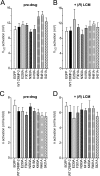
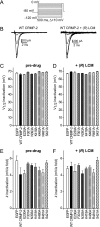
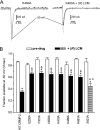
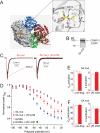
The anti-epileptic drug (R)-lacosamide ((2R)-2-(acetylamino)-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide (LCM)) modulates voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) by preferentially interacting with slow inactivated sodium channels, but the observation that LCM binds to collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2) suggests additional mechanisms of action for LCM. We postulated that CRMP-2 levels affects the actions of LCM on VGSCs. CRMP-2 labeling by LCM analogs was competitively displaced by excess LCM in rat brain lysates. Manipulation of CRMP-2 levels in the neuronal model system CAD cells affected slow inactivation of VGSCs without any effects on other voltage-dependent properties. In silico docking was performed to identify putative binding sites in CRMP-2 that may modulate the effects of LCM on VGSCs. These studies identified five cavities in CRMP-2 that can accommodate LCM. CRMP-2 alanine mutants of key residues within these cavities were functionally similar to wild-type CRMP-2 as assessed by similar levels of enhancement in dendritic complexity of cortical neurons. Next, we examined the effects of expression of wild-type and mutant CRMP-2 constructs on voltage-sensitive properties of VGSCs in CAD cells: 1) steady-state voltage-dependent activation and fast-inactivation properties were not affected by LCM, 2) CRMP-2 single alanine mutants reduced the LCM-mediated effects on the ability of endogenous Na(+) channels to transition to a slow inactivated state, and 3) a quintuplicate CRMP-2 alanine mutant further decreased this slow inactivated fraction. Collectively, these results identify key CRMP-2 residues that can coordinate LCM binding thus making it more effective on its primary clinical target.
Figures

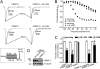
Similar articles
-
Drug binding assays do not reveal specific binding of lacosamide to collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2).CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Jun;18(6):493-500. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00313.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22672303 Free PMC article.
-
Lacosamide: a review of preclinical properties.CNS Drug Rev. 2007 Spring;13(1):21-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2007.00001.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 17461888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity of the anticonvulsant lacosamide in experimental and human epilepsy via selective effects on slow Na+ channel inactivation.Epilepsia. 2017 Jan;58(1):27-41. doi: 10.1111/epi.13602. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 27864845
-
Differential block of sensory neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels by lacosamide [(2R)-2-(acetylamino)-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide], lidocaine, and carbamazepine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Jul;326(1):89-99. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.133413. Epub 2008 Mar 31. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18378801
-
Specific binding of lacosamide to collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) and direct impairment of its canonical function: implications for the therapeutic potential of lacosamide.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;51(2):599-609. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8775-9. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24944082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRMPs: critical molecules for neurite morphogenesis and neuropsychiatric diseases.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Sep;20(9):1037-45. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.77. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26077693 Review.
-
mTORC1-dependent translation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 drives neuroadaptations underlying excessive alcohol-drinking behaviors.Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Jan;22(1):89-101. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.12. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 26952865 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of the CRMP2-neurofibromin complex on pain behaviors.Pain. 2017 Nov;158(11):2203-2221. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001026. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28767512 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation alters CRMP2 regulation of calcium influx in sensory neurons.Channels (Austin). 2013 May-Jun;7(3):153-9. doi: 10.4161/chan.24224. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Channels (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23510938 Free PMC article.
-
Development of lacosamide for the treatment of partial-onset seizures.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Jul;1291(1):56-68. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12213. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23859801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi D., Stables J. P., Kohn H. (1996) J. Med. Chem. 39, 1907–1916 - PubMed
-
- Perucca E., Yasothan U., Clincke G., Kirkpatrick P. (2008) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 973–974 - PubMed
-
- Harris J. A., Murphy J. A. (2009) Ann. Pharmacother. 43, 1809–1817 - PubMed
-
- Tilz C., Resch R., Hofer T., Eggers C. (2009) Epilepsia 51, 316–317 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

