Plasma volume, albumin, and fluid status in peritoneal dialysis patients
- PMID: 20538836
- PMCID: PMC2924416
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09411209
Plasma volume, albumin, and fluid status in peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients may be overhydrated especially when inflammation is present. We hypothesized that patients with a plasma albumin below the median value would have measurable overhydration without a proportional increase in plasma volume (PV).
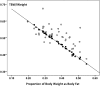
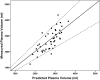
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We investigated a cross-sectional sample of 46 prevalent PD patients powered to detect a proportional increase in PV associated with whole body overhydration and hypoalbuminemia. PV was determined from (125)I-labeled albumin dilution, absolute total body water from D dilution (TBW(D)), and relative hydration from multifrequency bioimpedance analysis (BIA; Xitron 4200) expressed as the extracellular water (ECW):TBW(BIA) ratio.
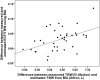
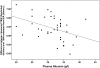
Results: Whereas patients with plasma albumin below the median (31.4 g/dl) were overhydrated as determined both by BIA alone (ECW:TBW(BIA) 0.49 versus 0.47, P < 0.036) and the difference between estimated TBW(BIA) and measured TBW(D) (3.55 versus 0.94 L, P = 0.012), corrected PV was not different (1463 versus 1482 ml/m(2), NS). Mean PV was not different from predicted, and its variance did not correlate with any other clinical measures. Multivariate analysis showed that the only independent predictor of whole body overhydration was reduced plasma albumin.
Conclusions: Hypoalbuminemia is an important determinant of tissue overhydration in PD patients. This overhydration is not associated with an increased plasma volume. Attempts to normalize the ECW:TBW ratio in hypoalbuminemic, inflamed PD patients may lead to hypovolemia and loss of residual renal function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of fluid status in peritoneal dialysis patients.Perit Dial Int. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6):683-92. Perit Dial Int. 2002. PMID: 12556070
-
Assessment of body composition using dry mass index and ratio of total body water to estimated volume based on bioelectrical impedance analysis in chronic kidney disease patients.J Ren Nutr. 2013 Jan;23(1):28-36. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2011.12.006. Epub 2012 Mar 9. J Ren Nutr. 2013. PMID: 22406124
-
Increase in Extracellular Hydration Status After Initiating Peritoneal Dialysis Electively.Perit Dial Int. 2017 May-Jun;37(3):338-340. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2016.00213. Perit Dial Int. 2017. PMID: 28512162
-
Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods.Med Eng Phys. 2008 Dec;30(10):1257-69. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Med Eng Phys. 2008. PMID: 18676172 Review.
-
Assessment of Hydration Status in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: Validity, Prognostic Value, Strengths, and Limitations of Available Techniques.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(8):589-612. doi: 10.1159/000509115. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32721969 Review.
Cited by
-
Intraperitoneal MASP-1 Levels are Associated with Peritoneal Solute Transport Rate in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 29;17:7807-7817. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S486011. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39494204 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance is associated with new-onset cardiovascular events in nondiabetic patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2014 Dec;33(4):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 26885476 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Trends and Clinical Impact of Malnutrition on In-Hospital Outcomes Among Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Inpatient Analysis.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 29;17(9):1508. doi: 10.3390/nu17091508. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362823 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Muscle Mass in the Integrated Assessment of Patients on Hemodialysis.Front Nutr. 2021 Aug 16;8:697523. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.697523. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34485360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of the deuterium abundances in water from 156 to 10,000 ppm by SIFT-MS.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011 Jan;22(1):179-86. doi: 10.1007/s13361-010-0019-2. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21472556
References
-
- Brown EA, Davies SJ, Rutherford P, Meeus F, Borras M, Riegel W, Divino Filho JC, Vonesh E, Van Bree M: Survival of functionally anuric patients on automated peritoneal dialysis: The European APD Outcome Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 2948–2957, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Davies SJ, Brown E, Riegel W, Clutterbuck E, Heimburger O, Vega Diaz N, Mellotte G, Perez-Contreras J, Scanziani R, D'Auzac C, Kuypers D, Divino Fiho JC: What is the link between poor ultrafiltration and increased mortality in anuric APD patients? Analysis of data from EAPOS. Perit Dial Int 26: 458–465, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Avila-Diaz M, Ventura MD, Valle D, Vicente-Martinez M, Garcia-Gonzalez Z, Cisneros A, Furlong MD, Gomez AM, Prado-Uribe MD, Amato D, Paniagua R: Inflammation and extracellular volume expansion are related to sodium and water removal in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 26: 574–580, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Davies SJ, Garcia Lopez E, Woodrow G, Donovan K, Plum J, Williams P, Johansson AC, Bosselmann HP, Heimburger O, Simonsen O, Davenport A, Lindholm B, Tranaeus A, Divino Filho JC: Longitudinal relationships between fluid status, inflammation, urine volume and plasma metabolites of icodextrin in patients randomized to glucose or icodextrin for the long exchange. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 2982–2988, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

