Attachment of mouse hepatitis virus to O-acetylated sialic acid is mediated by hemagglutinin-esterase and not by the spike protein
- PMID: 20538854
- PMCID: PMC2919023
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00566-10
Attachment of mouse hepatitis virus to O-acetylated sialic acid is mediated by hemagglutinin-esterase and not by the spike protein
Abstract
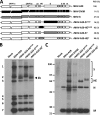
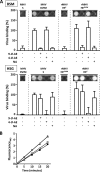
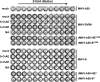
The members of Betacoronavirus phylocluster A possess two types of surface projections, one comprised of the spike protein (S) and the other of hemagglutinin-esterase (HE). Purportedly, these viruses bind to O-acetylated sialic acids (O-Ac-Sias) primarily through S, with HE serving merely as receptor-destroying enzyme. Here, we show that, in apparent contrast to human and ungulate host range variants of Betacoronavirus-1, murine coronaviruses actually bind to O-Ac-Sias via HE exclusively. Apparently, expansion of group A betacoronaviruses into new hosts and niches was accompanied by changes in HE ligand and substrate preference and in the roles of HE and S in Sia receptor usage.
Figures
References
-
- Callebaut, P. E., and M. B. Pensaert. 1980. Characterization and isolation of structural polypeptides in haemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 48:193-204. - PubMed
-
- Corfield, A. P., M. Sander-Wewer, R. W. Veh, M. Wember, and R. Schauer. 1986. The action of sialidases on substrates containing O-acetylsialic acids. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 367:433-439. - PubMed
-
- Dveksler, G. S., C. W. Dieffenbach, C. B. Cardellichio, K. McCuaig, M. N. Pensiero, G. S. Jiang, N. Beauchemin, and K. V. Holmes. 1993. Several members of the mouse carcinoembryonic antigen-related glycoprotein family are functional receptors for the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus A59. J. Virol. 67:1-8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

