Novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-derived peptide protects against impairment of cerebrovasodilation after photothrombosis through inhibition of JNK MAPK
- PMID: 20538898
- PMCID: PMC2928614
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00256.2010
Novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-derived peptide protects against impairment of cerebrovasodilation after photothrombosis through inhibition of JNK MAPK
Abstract
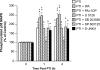
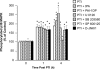
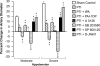
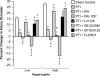
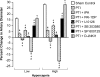
The sole FDA-approved treatment for acute stroke is recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rtPA). However, rtPA aggravates the impairment of cerebrovasodilation induced by global hypoxia/ischemia; this impairment is attenuated by the preinjury treatment with the plasminogen activator inhibitor derivative EEIIMD. MAPK (a family of kinases, p38, and JNK) is upregulated after cerebral ischemia. In this study, we determined whether the novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-derived peptide, Ac-RMAPEEIIMDRPFLYVVR-amide, (PAI-1-DP) given 30 min before or 2 h after, focal central nervous system injury induced by photothrombosis would preserve responses to cerebrovasodilators and the role of p38 and JNK MAPK in such effects. Cerebrospinal fluid JNK and p38 levels were elevated by photothrombotic injury, an effect potentiated by rtPA. Cerebrovasodilation was blunted by photothrombosis and reversed to vasoconstriction by rtPA but restored to dilation by PAI-1-DP pre- and posttreatment. PAI-1-DP blocked JNK, but preserved p38 MAPK upregulation after photothrombosis. The JNK MAPK antagonist SP600125 prevented, and the p38 antagonist SB203580 potentiated, impaired cerebrovasodilation after photothrombosis. These data indicate that rtPA impairs cerebrovasodilation after injury by activating JNK, while p38 MAPK is protective, and that the novel peptide PAI-1-DP protects by inhibiting activation of JNK by rtPA. JNK MAPK inhibitors, including PAI-1-DP, may offer a novel approach to increase the benefit-to-risk ratio of thrombolytic therapy and enable its use in central nervous system ischemic disorders.
Figures

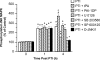

Similar articles
-
PAI-1-derived peptide EEIIMD prevents impairment of cerebrovasodilation by augmenting p38 MAPK upregulation after cerebral hypoxia/ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):H76-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00185.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20435843 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cell-coupled tissue plasminogen activator prevents impairment of cerebral vasodilatory responses through inhibition of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase and potentiation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase after cerebral photothrombosis in the newborn pig.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov;12(6):e369-75. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181fe40a7. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21037505 Free PMC article.
-
tPA contributes to impaired NMDA cerebrovasodilation after traumatic brain injury through activation of JNK MAPK.Neurol Res. 2011 Sep;33(7):726-33. doi: 10.1179/016164110X12807570509853. Neurol Res. 2011. PMID: 21756552 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy with glucagon and a novel plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-derived peptide enhances protection against impaired cerebrovasodilation during hypotension after traumatic brain injury through inhibition of ERK and JNK MAPK.Neurol Res. 2012 Jul;34(6):530-7. doi: 10.1179/1743132812Y.0000000039. Epub 2012 May 30. Neurol Res. 2012. PMID: 22642975 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and thrombotic cerebrovascular diseases.Stroke. 2012 Oct;43(10):2833-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.622217. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22879095 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Targeting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in tetracycline-induced pleural injury in rabbits.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):L54-L68. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00579.2016. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28860148 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PAI-1 Mechanism with a Small Peptide Increases the Efficacy of Alteplase in a Rabbit Model of Chronic Empyema.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 14;15(5):1498. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051498. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242740 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of efficacy and safety of Reteplase and Alteplase in the treatment of hyper-acute cerebral infarction.Biosci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;38(1):BSR20170730. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170730. Print 2018 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29263145 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of Porcine Stroke Models to Bridge the Gap from Pre-Clinical Findings to Clinical Implementation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 8;21(18):6568. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186568. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32911769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision targeting of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 mechanism increases efficacy of fibrinolytic therapy in empyema.Physiol Rep. 2021 May;9(9):e14861. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14861. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33991465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akkawi S, Nassar T, Tarshis M, Cines DB, Higazi AAR. LRP and avB3 mediate tPA- activation of smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291: H1351–H1359, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Cines DB, Higazi AA. Plasminogen activators contribute to impairment of hypercapnic and hypotensive cerebrovasodilation after cerebral hypoxia/ischemia in the newborn pig. Stroke 36: 2265–2269, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Cines DB, Higazi AAR. Plasminogen activators contribute to age dependent impairment of NMDA cerebrovasodilation after brain injury. Dev Brain Res 156: 139–146, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Nassar T, Akkawi S, Smith DH, Chen XH, Cines DB, Higazi AAR. Neutralizing the neurotoxic effects of exogenous and endogenous tPA. Nat Neurosci 9: 1150–1157, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

