Interaction between PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 through their transmembrane domains is required for localization of PKD2L1 at taste pores in taste cells of circumvallate and foliate papillae
- PMID: 20538909
- PMCID: PMC2996907
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-162925
Interaction between PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 through their transmembrane domains is required for localization of PKD2L1 at taste pores in taste cells of circumvallate and foliate papillae
Abstract
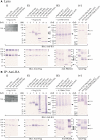
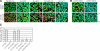
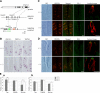
The polycystic kidney disease 1-like 3 (PKD1L3) and polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1 (PKD2L1) proteins have been proposed to form heteromers that function as sour taste receptors in mammals. Here, we show that PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 interact through their transmembrane domains, and not through the coiled-coil domain, by coimmunoprecipitation experiments using a series of deletion mutants. Deletion mutants lacking the critical interaction region were not transported to the cell surface and remained in the cytoplasm, whereas PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 proteins were expressed at the cell surface when both are transfected. Calcium imaging analysis revealed that neither the coiled-coil domain nor the EF-hand domain located in the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of PKD2L1 was required for response on stimulation with an acidic solution. Finally, PKD2L1 did not localize to the taste pore but was distributed throughout the cytoplasm in taste cells of circumvallate and foliate papillae in PKD1L3(-/-) mice, whereas it localized to the taste pore in wild-type mice. Collectively, these results suggest that the interaction between PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 through their transmembrane domains is essential for proper trafficking of the channels to the cell surface in taste cells of circumvallate and foliate papillae and in cultured cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of polycystic kidney disease-2-like 1 (PKD2L1)-PKD1L3 complex by acid in mouse taste cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 4;285(23):17277-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C110.132944. Epub 2010 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20406802 Free PMC article.
-
The response of PKD1L3/PKD2L1 to acid stimuli is inhibited by capsaicin and its pungent analogs.FEBS J. 2012 May;279(10):1857-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08566.x. Epub 2012 Apr 16. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22420714 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential family members PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 form a candidate sour taste receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12569-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602702103. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16891422 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels and taste sensation.J Dent Res. 2009 Mar;88(3):212-8. doi: 10.1177/0022034508330212. J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19329452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acid-sensing ion channels in taste buds.Arch Histol Cytol. 2006 Dec;69(4):227-31. doi: 10.1679/aohc.69.227. Arch Histol Cytol. 2006. PMID: 17287577 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TRPP3 Channel Function by N-terminal Domain Palmitoylation and Phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 2;291(49):25678-25691. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756544. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27754867 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-induced off-response of PKD2L1 channel in Xenopus oocytes and its regulation by Ca(2.).Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 27;5:15752. doi: 10.1038/srep15752. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26502994 Free PMC article.
-
Bimodal effect of alkalization on the polycystin transient receptor potential channel, PKD2L1.Pflugers Arch. 2011 May;461(5):507-13. doi: 10.1007/s00424-011-0934-5. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Pflugers Arch. 2011. PMID: 21340459
-
Characterization of host factors associated with the internal ribosomal entry sites of foot-and-mouth disease and classical swine fever viruses.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 25;12(1):6709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10437-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35468926 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced β-adrenergic response in mice with dominant-negative expression of the PKD2L1 channel.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 20;17(1):e0261668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261668. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35051185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delmas P., Padilla F., Osorio N., Coste B., Raoux M., Crest M. (2004) Polycystins, calcium signaling, and human diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 322, 1374–1383 - PubMed
-
- LopezJimenez N. D., Cavenagh M. M., Sainz E., Cruz-Ithier M. A., Battey J. F., Sullivan S. L. (2006) Two members of the TRPP family of ion channels, Pkd1l3 and Pkd2l1, are co-expressed in a subset of taste receptor cells. J. Neurochem. 98, 68–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

