Crystal structure and ligand binding of the MID domain of a eukaryotic Argonaute protein
- PMID: 20539312
- PMCID: PMC2897117
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2010.81
Crystal structure and ligand binding of the MID domain of a eukaryotic Argonaute protein
Abstract
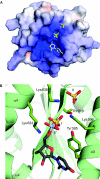
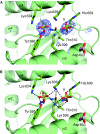
Argonaute (AGO) proteins are core components of RNA-induced silencing complexes and have essential roles in RNA-mediated gene silencing. They are characterized by a bilobal architecture, consisting of one lobe containing the amino-terminal and PAZ domains and another containing the MID and PIWI domains. Except for the PAZ domain, structural information on eukaryotic AGO domains is not yet available. In this study, we report the crystal structure of the MID domain of the eukaryotic AGO protein QDE-2 from Neurospora crassa. This domain adopts a Rossmann-like fold and recognizes the 5'-terminal nucleotide of a guide RNA in a manner similar to its prokaryotic counterparts. The 5'-nucleotide-binding site shares common residues with a second, adjacent ligand-binding site, suggesting a mechanism for the cooperative binding of ligands to the MID domain of eukaryotic AGOs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Argonaute MID domain takes centre stage.EMBO Rep. 2010 Aug;11(8):564-5. doi: 10.1038/embor.2010.110. Epub 2010 Jul 16. EMBO Rep. 2010. PMID: 20634804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broennimann C et al. (2006) The PILATUS 1M detector. J Synchrotron Radiat 13: 120–130 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

