MiR-RACE, a new efficient approach to determine the precise sequences of computationally identified trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata) microRNAs
- PMID: 20539756
- PMCID: PMC2881865
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010861
MiR-RACE, a new efficient approach to determine the precise sequences of computationally identified trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata) microRNAs
Abstract
Background: Among the hundreds of genes encoding miRNAs in plants reported, much more were predicted by numerous computational methods. However, unlike protein-coding genes defined by start and stop codons, the ends of miRNA molecules do not have characteristics that can be used to define the mature miRNAs exactly, which made computational miRNA prediction methods often cannot predict the accurate location of the mature miRNA in a precursor with nucleotide-level precision. To our knowledge, there haven't been reports about comprehensive strategies determining the precise sequences, especially two termini, of these miRNAs.
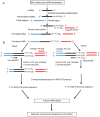
Methods: In this study, we report an efficient method to determine the precise sequences of computationally predicted microRNAs (miRNAs) that combines miRNA-enriched library preparation, two specific 5' and 3' miRNA RACE (miR-RACE) PCR reactions, and sequence-directed cloning, in which the most challenging step is the two specific gene specific primers designed for the two RACE reactions. miRNA-mediated mRNA cleavage by RLM-5' RACE and sequencing were carried out to validate the miRNAs detected. Real-time PCR was used to analyze the expression of each miRNA.
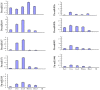
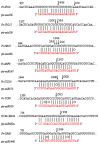
Results: The efficiency of this newly developed method was validated using nine trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata) miRNAs predicted computationally. The miRNAs computationally identified were validated by miR-RACE and sequencing. Quantitative analysis showed that they have variable expression. Eight target genes have been experimentally verified by detection of the miRNA-mediated mRNA cleavage in Poncirus trifoliate.
Conclusion: The efficient and powerful approach developed herein can be successfully used to validate the sequences of miRNAs, especially the termini, which depict the complete miRNA sequence in the computationally predicted precursor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of regulatory mechanism of Poncirus trifoliata microRNAs on their target genes with an integrated strategy of newly developed PPM-RACE and RLM-RACE.Gene. 2014 Feb 1;535(1):42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.069. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24275346
-
A method for validating microRNAs in plants by miR-RACE.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1287:139-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2453-0_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25740362
-
Identification of miRNAs and their target genes using deep sequencing and degradome analysis in trifoliate orange [Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf] [corrected].Mol Biotechnol. 2012 May;51(1):44-57. doi: 10.1007/s12033-011-9439-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 21796478
-
miR-RACE: an effective approach to accurately determine the sequence of computationally identified miRNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1296:109-18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2547-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25791595
-
Deep sequencing discovery of novel and conserved microRNAs in trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliata).BMC Genomics. 2010 Jul 13;11:431. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-431. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20626894 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification and expression profiling of miRNAs in two color variants of carrot (Daucus carota L.) using deep sequencing.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 7;14(3):e0212746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212746. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30845212 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA Sequencing Reveals Differential miRNA Expression in the Early Development of Broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) Pollen.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 24;8:404. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00404. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28392797 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, evolution, and expression partitioning of miRNAs in allopolyploid Brassica napus.J Exp Bot. 2015 Dec;66(22):7241-53. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv420. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 26357884 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of potential conserved microRNAs and their targets in peach (Prunus persica).Mol Cells. 2012 Sep;34(3):239-49. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0004-7. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22878892 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of grapevine microR164 and its target genes.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Oct;39(10):9463-72. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1811-9. Epub 2012 Jun 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22733489
References
-
- Ruvkun G, Wightman B, Ha I. The 20 years it took to recognize the importance of tiny RNAs. Cell. 2004;116:s93–s96. - PubMed
-
- Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:19–53. - PubMed
-
- Mallory AC, Bouché N. MicroRNA-directed regulation to cleave or not to cleave. Trends in Plant Science. 2008;13:359–367. - PubMed
-
- Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science. 2008;320:1185–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

