Targeted probes for cardiovascular MRI
- PMID: 20539821
- PMCID: PMC2882676
- DOI: 10.4155/FMC.09.154
Targeted probes for cardiovascular MRI
Abstract
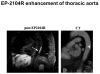
Molecular MRI plays an important role in studying molecular and cellular processes associated with heart disease. Targeted probes that recognize important biomarkers of atherosclerosis, apoptosis, necrosis, angiogenesis, thrombosis and inflammation have been developed. This review discusses the properties of chemically different contrast agents including iron oxide nanoparticles, gadolinium-based nanoparticles or micelles, discrete peptide conjugates and activatable probes. Numerous examples of contrast agents based on these approaches have been used in preclinical MRI of cardiovascular diseases. Clinical applications are still under investigation for some selected agents with highly promising initial results. Molecular MRI shows great potential for the detection and characterization of a wide range of cardiovascular diseases, as well as for monitoring response to therapy.
Keywords: Cardiovascular; MRI; atherosclerosis; gadolinium; iron oxide nanoparticles; micelles; molecular imaging; smart probes; targeted peptides.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Hybrid, metal oxide-peptide amphiphile micelles for molecular magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerosis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Nov 15;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0420-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30442135 Free PMC article.
-
Iron oxide nanoparticle-micelles (ION-micelles) for sensitive (molecular) magnetic particle imaging and magnetic resonance imaging.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057335. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437371 Free PMC article.
-
MRI probes for sensing biologically relevant metal ions.Future Med Chem. 2010 Mar;2(3):367-84. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.161. Future Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21426172 Review.
-
Emerging engineered magnetic nanoparticulate probes for targeted MRI of atherosclerotic plaque macrophages.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012 May;7(5):735-49. doi: 10.2217/nnm.12.46. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22630154 Review.
-
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications.Future Med Chem. 2010 Mar;2(3):427-49. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.164. Future Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21426176 Review.
Cited by
-
Coupling Gd‑DTPA with a bispecific, recombinant protein anti‑EGFR‑iRGD complex improves tumor targeting in MRI.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jun;35(6):3227-35. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4712. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27035336 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, purification, and characterization of lanthanide complexes for use as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging.J Vis Exp. 2011 Jul 21;(53):2844. doi: 10.3791/2844. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21808225 Free PMC article.
-
Activatable T₁ and T₂ magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents.Ann Biomed Eng. 2011 Apr;39(4):1335-48. doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0270-0. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011. PMID: 21331662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel MRI contrast agent NaGdF4@PEG-CLS@MMP-13 NPs for detecting articular cartilage injury.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 20;15(1):6251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89444-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39979429 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Citrate-Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;14(4):354. doi: 10.3390/nano14040354. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caravan P, Lauffer RB. Contrast Agents: Basic Principles. In: Edelman RR, Hesselink JR, Zlatkin MB, Crues JV, editors. Clinical Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Saunders; Philadelphia, USA: 2005. pp. 357–375.
-
- Thomson LE, Kim RJ, Judd RM. Magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of myocardial viability. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;19(6):771–788. - PubMed
-
- Goyen M, Edelman M, Perreault P, et al. MR angiography of aortoiliac occlusive disease: a phase III study of the safety and effectiveness of the blood-pool contrast agent MS-325. Radiology. 2005;236(3):825–833. - PubMed
-
- Caravan P, Parigi G, Chasse JM, et al. Albumin Binding, Relaxivity, and Water Exchange Kinetics of the Diastereoisomers of MS-325, a Gadolinium(III)-Based Magnetic Resonance Angiography Contrast Agent. Inorg Chem. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Eldredge HB, Spiller M, Chasse JM, Greenwood MT, Caravan P. Species dependence on plasma protein binding and relaxivity of the gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent MS-325. Invest Radiol. 2006;41(3):229–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
