Hydrogen sulphide induces micro opioid receptor-dependent analgesia in a rodent model of visceral pain
- PMID: 20540729
- PMCID: PMC2908066
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-36
Hydrogen sulphide induces micro opioid receptor-dependent analgesia in a rodent model of visceral pain
Abstract
Background: Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is a gaseous neuro-mediator that exerts analgesic effects in rodent models of visceral pain by activating KATP channels. A body of evidence support the notion that KATP channels interact with endogenous opioids. Whether H2S-induced analgesia involves opioid receptors is unknown.
Methods: The perception of painful sensation induced by colorectal distension (CRD) in conscious rats was measured by assessing the abdominal withdrawal reflex. The contribution of opioid receptors to H2S-induced analgesia was investigated by administering rats with selective mu, kappa and delta opioid receptor antagonists and antisenses. To investigate whether H2S causes mu opioid receptor (MOR) transactivation, the neuronal like cells SKNMCs were challenged with H2S in the presence of MOR agonist (DAMGO) or antagonist (CTAP). MOR activation and phosphorylation, its association to beta arrestin and internalization were measured.
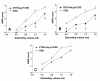
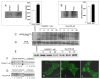
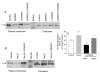
Results: H2S exerted a potent analgesic effects on CRD-induced pain. H2S-induced analgesia required the activation of the opioid system. By pharmacological and molecular analyses, a robust inhibition of H2S-induced analgesia was observed in response to central administration of CTAP and MOR antisense, while kappa and delta receptors were less involved. H2S caused MOR transactivation and internalization in SKNMCs by a mechanism that required AKT phosphorylation. MOR transactivation was inhibited by LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, and glibenclamide, a KATP channels blocker.
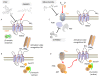
Conclusions: This study provides pharmacological and molecular evidence that antinociception exerted by H2S in a rodent model of visceral pain is modulated by the transactivation of MOR. This observation provides support for development of new pharmacological approaches to visceral pain.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

