Analysis of the vp2 gene sequence of a new mutated mink enteritis parvovirus strain in PR China
- PMID: 20540765
- PMCID: PMC2903559
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-124
Analysis of the vp2 gene sequence of a new mutated mink enteritis parvovirus strain in PR China
Abstract
Background: Mink enteritis virus (MEV) causes a highly contagious viral disease of mink with a worldwide distribution. MEV has a linear, single-stranded, negative-sense DNA with a genome length of approximately 5,000 bp. The VP2 protein is the major structural protein of the parvovirus encoded by the vp2 gene. VP2 is highly antigenic and plays important roles in determining viral host ranges and tissue tropisms. This study describes the bionomics and vp2 gene analysis of a mutated strain, MEV-DL, which was isolated recently in China and outlines its homologous relationships with other selected strains registered in Genbank.
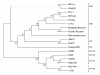
Results: The MEV-DL strain can infect F81 cells with cytopathic effects. Pig erythrocytes were agglutinated by the MEV-DL strain. The generation of MEV-DL in F81 cells could infect mink within three months and cause a disease that was similar to that caused by wild-type MEV. A comparative analysis of the vp2 gene nucleotide (nt) sequence of MEV-DL showed that this was more than 99% homologous with other mink enteritis parvoviruses in Genbank. However, the nucleotide residues at positions 1,065 and 1,238 in the MEV-DL strain of the vp2 gene differed from those of all the other MEV strains described previously. It is noteworthy that the mutation at the nucleotide residues position 1,238 led to Asp/Gly replacement. This may lead to structural changes. A phylogenetic tree and sequence distance table were obtained, which showed that the MEV-DL and ZYL-1 strains had the closest inheritance distance.
Conclusions: A new variation of the vp2 gene exists in the MEV-DL strain, which may lead to structural changes of the VP2 protein. Phylogenetic analysis showed that MEV-DL may originate from the ZYL-1 strain in DaLian.
Figures

References
-
- Tingxiu Jiang, Houkun Pu, Long Wang. Preliminary report about Mink viral enteritis disease. Fur animals. 1981;2:224.
-
- Brown TT Jr, Paul PS, Mengeling WL. Response of conventionally raised weanling pigs to experimental infection with a virulent strain of porcine parvovirus. Am J Vet Res. 1980;41:1221–1224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

