Integrative genomic and proteomic analyses identify targets for Lkb1-deficient metastatic lung tumors
- PMID: 20541700
- PMCID: PMC2901842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.04.026
Integrative genomic and proteomic analyses identify targets for Lkb1-deficient metastatic lung tumors
Abstract
In mice, Lkb1 deletion and activation of Kras(G12D) results in lung tumors with a high penetrance of lymph node and distant metastases. We analyzed these primary and metastatic de novo lung cancers with integrated genomic and proteomic profiles, and have identified gene and phosphoprotein signatures associated with Lkb1 loss and progression to invasive and metastatic lung tumors. These studies revealed that SRC is activated in Lkb1-deficient primary and metastatic lung tumors, and that the combined inhibition of SRC, PI3K, and MEK1/2 resulted in synergistic tumor regression. These studies demonstrate that integrated genomic and proteomic analyses can be used to identify signaling pathways that may be targeted for treatment.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


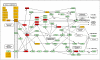

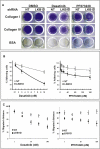
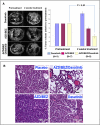
Comment in
-
LKB1 and Src: antagonistic regulators of tumor growth and metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2010 Jun 15;17(6):527-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.016. Cancer Cell. 2010. PMID: 20541695
References
-
- Al-Shahrour F, Diaz-Uriarte R, Dopazo J. FatiGO: a web tool for finding significant associations of Gene Ontology terms with groups of genes. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:578–580. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. - PubMed
-
- Arthur WT, Petch LA, Burridge K. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol. 2000;10:719–722. - PubMed
-
- Bild AH, Yao G, Chang JT, Wang Q, Potti A, Chasse D, Joshi MB, Harpole D, Lancaster JM, Berchuck A, et al. Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to targeted therapies. Nature. 2006;439:353–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 1RC2CA147940-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA137008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137181/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG2400401/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA142794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141576/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA141576/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 GRANT CA120060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

