Building RNA-protein granules: insight from the germline
- PMID: 20541937
- PMCID: PMC2929181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.05.004
Building RNA-protein granules: insight from the germline
Abstract
The germline originates from primordial embryonic germ cells which give rise to sperm and egg cells and consequently, to the next generation. Germ cells of many organisms contain electron-dense granules that comprise RNA and proteins indispensable for germline development. Here we review recent reports that provide important insights into the structure and function of crucial RNA and protein components of the granules, including DEAD-box helicases, Tudor domain proteins, Piwi/Argonaute proteins and piRNA. Collectively, these components function in translational control, remodeling of ribonucleoprotein complexes and transposon silencing. Furthermore, they interact with each other by means of conserved structural modules and post-translationally modified amino acids. These data suggest a widespread use of several protein motifs in germline development and further our understanding of other ribonucleoprotein structures, for example, processing bodies and neuronal granules.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
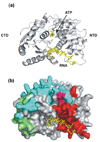
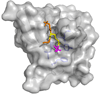
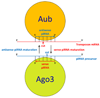

References
-
- Cinalli RM, et al. Germ cells are forever. Cell. 2008;132:559–562. - PubMed
-
- Seydoux G, Braun RE. Pathway to totipotency: lessons from germ cells. Cell. 2006;127:891–904. - PubMed
-
- Mahowald AP. Assembly of the Drosophila germ plasm. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2001;203:187–213. - PubMed
-
- Kloc M, et al. The Balbiani body and germ cell determinants: 150 years later. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2004;59:1–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

