microRNAs: a role in drug resistance in parasitic nematodes?
- PMID: 20541972
- PMCID: PMC2930248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.05.003
microRNAs: a role in drug resistance in parasitic nematodes?
Abstract
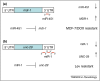
Drug resistance in parasitic nematodes is an increasing problem worldwide, with resistance reported to all three commonly used classes of anthelmintics. Most studies to date have sought to correlate the resistant phenotype with genotypic changes in putative target molecules. Although this approach has identified mutations in several relevant genes, resistance might result from a complex interaction of different factors. Here we propose an alternative mechanism underlying the development of drug resistance based on functional differences in microRNA activity in resistant parasites. microRNAs play an important role in resistance to chemotherapeutic agents in many tumour cells and here we discuss whether they might also be involved in anthelmintic resistance in parasitic nematodes.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased Expression of a MicroRNA Correlates with Anthelmintic Resistance in Parasitic Nematodes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 6;7:452. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00452. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29209592 Free PMC article.
-
Nematode parasites of animals are more prone to develop xenobiotic resistance than nematode parasites of plants.Parasite. 2004 Jun;11(2):119-29. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2004112119. Parasite. 2004. PMID: 15224572
-
Anthelmintic resistance.Vet Parasitol. 1994 Aug;54(1-3):259-68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(94)90094-9. Vet Parasitol. 1994. PMID: 7846855 Review.
-
Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: a status report.Trends Parasitol. 2004 Oct;20(10):477-81. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2004.08.001. Trends Parasitol. 2004. PMID: 15363441 Review.
-
Discovery of genomic intervals that underlie nematode responses to benzimidazoles.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Mar 30;12(3):e0006368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006368. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29601575 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrative genomic, proteomic and phenotypic studies of Leishmania donovani strains revealed genetic features associated with virulence and antimony-resistance.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Oct 12;13(1):510. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04397-4. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 33046138 Free PMC article.
-
Nematode endogenous small RNA pathways.Worm. 2014 Mar 5;3:e28234. doi: 10.4161/worm.28234. eCollection 2014. Worm. 2014. PMID: 25340013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of circulating parasite-derived microRNAs in filarial infections.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jul 17;8(7):e2971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002971. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25033073 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative characterization of microRNAs in Schistosoma japonicum schistosomula from Wistar rats and BALB/c mice.Parasitol Res. 2015 Jul;114(7):2639-47. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4468-1. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 25895062
-
microRNAs in parasites and parasite infection.RNA Biol. 2013 Mar;10(3):371-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.23716. Epub 2013 Feb 7. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23392243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourguinat C. P-glycoprotein-like protein, a possible genetic marker for ivermectin resistance selection in Onchocerca volvulus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008;158:101–111. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan R.M. Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: a status report. Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:477–481. - PubMed
-
- Gasbarre L.C. The identification of cattle nematode parasites resistant to multiple classes of anthelmintics in a commercial cattle population in the US. Vet. Parasitol. 2009;166:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Sargison N. Multiple anthelmintic resistance in sheep. Vet. Record. 2001;149:778–779. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwhof G.J., Bishop S.C. Costs of the major endemic diseases of sheep in Great Britain and the potential benefits of reduction in disease impact. Anim. Sci. 2005;81:23–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

