A ubiquitin-binding domain in Cockayne syndrome B required for transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 20541997
- PMCID: PMC2885502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.04.017
A ubiquitin-binding domain in Cockayne syndrome B required for transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
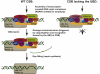
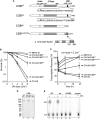
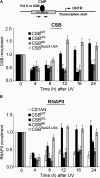
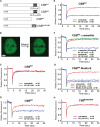
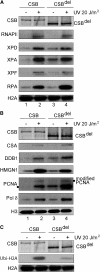
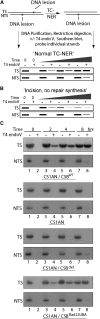
Transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER) allows RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)-blocking lesions to be rapidly removed from the transcribed strand of active genes. Defective TCR in humans is associated with Cockayne syndrome (CS), typically caused by defects in either CSA or CSB. Here, we show that CSB contains a ubiquitin-binding domain (UBD). Cells expressing UBD-less CSB (CSB(del)) have phenotypes similar to those of cells lacking CSB, but these can be suppressed by appending a heterologous UBD, so ubiquitin binding is essential for CSB function. Surprisingly, CSB(del) remains capable of assembling nucleotide excision repair factors and repair synthesis proteins around damage-stalled RNAPII, but such repair complexes fail to excise the lesion. Together, our results indicate an essential role for protein ubiquitylation and CSB's UBD in triggering damage incision during TC-NER and allow us to integrate the function of CSA and CSB in a model for the process.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Ubiquitin recognition by the Cockayne syndrome group B protein: binding will set you free.Mol Cell. 2010 Jun 11;38(5):621-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.025. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20541993
References
-
- Anindya R., Aygun O., Svejstrup J.Q. Damage-induced ubiquitylation of human RNA polymerase II by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, but not Cockayne syndrome proteins or BRCA1. Mol. Cell. 2007;28:386–397. - PubMed
-
- Bienko M., Green C.M., Crosetto N., Rudolf F., Zapart G., Coull B., Kannouche P., Wider G., Peter M., Lehmann A.R. Ubiquitin-binding domains in Y-family polymerases regulate translesion synthesis. Science. 2005;310:1821–1824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

