Structure of the human mTOR complex I and its implications for rapamycin inhibition
- PMID: 20542007
- PMCID: PMC2887672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.017
Structure of the human mTOR complex I and its implications for rapamycin inhibition
Abstract
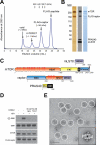
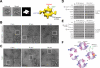
The mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) regulates cell growth in response to the nutrient and energy status of the cell, and its deregulation is common in human cancers. Little is known about the overall architecture and subunit organization of this essential signaling complex. We have determined the three-dimensional (3D) structure of the fully assembled human mTORC1 by cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Our analyses reveal that mTORC1 is an obligate dimer with an overall rhomboid shape and a central cavity. The dimeric interfaces are formed by interlocking interactions between the mTOR and raptor subunits. Extended incubation with FKBP12-rapamycin compromises the structural integrity of mTORC1 in a stepwise manner, leading us to propose a model in which rapamycin inhibits mTORC1-mediated phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and S6K1 through different mechanisms.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adami A, Garcia-Alvarez B, Arias-Palomo E, Barford D, Llorca O. Structure of TOR and its complex with KOG1. Mol Cell. 2007;27:509–516. - PubMed
-
- Choi JW, Chen J, Schreiber SL, Clardy J. Structure of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex interacting with the binding domain of human FRAP. Science. 1996;273:239–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

