Mechanism for the protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death
- PMID: 20542495
- PMCID: PMC2938064
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.06.002
Mechanism for the protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death
Abstract
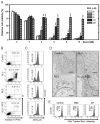
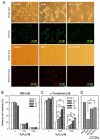
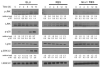
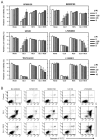
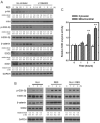
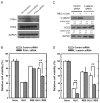
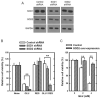
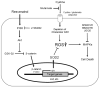
Oxidative stress can induce cytotoxicity in neurons, which plays an important role in the etiology of neuronal damage and degeneration. This study sought to determine the cellular and biochemical mechanisms underlying resveratrol's protective effect against oxidative neuronal death. Cultured HT22 cells, an immortalized mouse hippocampal neuronal cell line, were used as an in vitro model, and oxidative stress and neurotoxicity were induced in these neuronal cells by exposure to high concentrations of glutamate. Resveratrol strongly protected HT22 cells from glutamate-induced oxidative cell death. Resveratrol's neuroprotective effect was independent of its direct radical scavenging property, but instead was dependent on its ability to selectively induce the expression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (SOD2) and, subsequently, reduce mitochondrial oxidative stress and damage. The induction of mitochondrial SOD2 by resveratrol was mediated through the activation of the PI3K/Akt and GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Taken together, the results of this study show that up-regulation of mitochondrial SOD2 by resveratrol represents an important mechanism for its protection of neuronal cells against oxidative cytotoxicity resulting from mitochondrial oxidative stress.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 expression in neuroprotection by piceatannol, a natural analog and a metabolite of resveratrol, against glutamate-mediated oxidative injury in HT22 neuronal cells.Amino Acids. 2013 Aug;45(2):393-401. doi: 10.1007/s00726-013-1518-9. Epub 2013 May 28. Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 23712764
-
Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase SOD2, but not cytosolic SOD1, plays a critical role in protection against glutamate-induced oxidative stress and cell death in HT22 neuronal cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Mar 15;48(6):821-30. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.12.024. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20060889 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of 2,3,5,4'-tetrahydoxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside from Polygonum multiflorum against glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in HT22 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 4;195:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27939422
-
Pathways for ischemic cytoprotection: role of sirtuins in caloric restriction, resveratrol, and ischemic preconditioning.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Apr;31(4):1003-19. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.229. Epub 2011 Jan 12. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011. PMID: 21224864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial protection by resveratrol.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011 Jul;39(3):128-32. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e3182141f80. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011. PMID: 21383627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol up-regulates AMPA receptor expression via AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated protein translation.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Aug;95:144-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25791529 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Activity of Methanolic Extract of Lysimachia christinae against Glutamate Toxicity in HT22 Cell and Its Protective Mechanisms.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jan 13;2020:5352034. doi: 10.1155/2020/5352034. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32419811 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Gallocatechin Gallate on Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Stress in Hippocampal HT22 Cells.Molecules. 2021 Mar 4;26(5):1387. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051387. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33806640 Free PMC article.
-
Procyanidin A1 from Peanut Skin Exerts Anti-Aging Effects and Attenuates Senescence via Antioxidative Stress and Autophagy Induction.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;14(3):322. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030322. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227314 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of resveratrol in in vitro and in vivo experimental cerebral stroke models.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Aug 21;4(8):1151-62. doi: 10.1021/cn400094w. Epub 2013 Jun 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23758534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P. Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 1993;262:689–695. - PubMed
-
- Blandini F, Porter RH, Greenamyre JT. Glutamate and Parkinson’s desease. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996;12:73–94. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of nervous system. Neuron. 1988;1:623–634. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW. Exitotoxic cell death. J. Neurobiol. 1992;23:1261–1276. - PubMed
-
- Murphy TH, Miyamoto M, Sastre A, Schnaar RL, Coyle JT. Glutamate toxicity in neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron. 1989;2:1547–1558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

