CPHmodels-3.0--remote homology modeling using structure-guided sequence profiles
- PMID: 20542909
- PMCID: PMC2896139
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq535
CPHmodels-3.0--remote homology modeling using structure-guided sequence profiles
Abstract
CPHmodels-3.0 is a web server predicting protein 3D structure by use of single template homology modeling. The server employs a hybrid of the scoring functions of CPHmodels-2.0 and a novel remote homology-modeling algorithm. A query sequence is first attempted modeled using the fast CPHmodels-2.0 profile-profile scoring function suitable for close homology modeling. The new computational costly remote homology-modeling algorithm is only engaged provided that no suitable PDB template is identified in the initial search. CPHmodels-3.0 was benchmarked in the CASP8 competition and produced models for 94% of the targets (117 out of 128), 74% were predicted as high reliability models (87 out of 117). These achieved an average RMSD of 4.6 A when superimposed to the 3D structure. The remaining 26% low reliably models (30 out of 117) could superimpose to the true 3D structure with an average RMSD of 9.3 A. These performance values place the CPHmodels-3.0 method in the group of high performing 3D prediction tools. Beside its accuracy, one of the important features of the method is its speed. For most queries, the response time of the server is <20 min. The web server is available at http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/CPHmodels/.
Figures
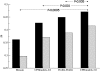
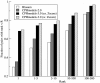

References
-
- Bennett-Lovsey RM, Herbert AD, Sternberg MJE, Kelley LA. Exploring the extremes of sequence/structure space with ensemble fold recognition in the program Phyre. Proteins. 2008;70:611–625. - PubMed
-
- Petersen TN, Lundegaard C, Nielsen M, Bohr H, Bohr J, Brunak S, Gippert GP, Lund O. Prediction of protein secondary structure at 80% accuracy. Proteins. 2000;41:17–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

