Neurotrophic and neuroimmune responses to early-life Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in rat lungs
- PMID: 20543002
- PMCID: PMC2951071
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00017.2010
Neurotrophic and neuroimmune responses to early-life Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in rat lungs
Abstract
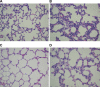
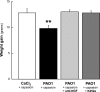
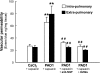
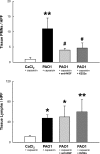
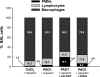
Early-life respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa is common in children with cystic fibrosis or immune deficits. Although many of its clinical manifestations involve neural reflexes, little information is available on the peripheral nervous system of infected airways. This study sought to determine whether early-life infection triggers a neurogenic-mediated immunoinflammatory response, the mechanisms of this response, and its relationship with other immunoinflammatory pathways. Weanling and adult rats were inoculated with suspensions containing P. aeruginosa (PAO1) coated on alginate microspheres suspended in Tris-CaCl(2) buffer. Five days after infection, rats were injected with capsaicin to stimulate nociceptive nerves in the airway mucosa, and microvascular permeability was measured using Evans blue as a tracer. PAO1 increased neurogenic inflammation in the extra- and intrapulmonary compartments of weanlings but not in adults. The mechanism involves selective overexpression of NGF, which is critical for the local increase in microvascular permeability and for the infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes into infected lung parenchyma. These effects are mediated in part by induction of downstream inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, especially IL-1beta, IL-18, and leptin. Our data suggest that neurogenic-mediated immunoinflammatory mechanisms play important roles in airway inflammation and hyperreactivity associated with P. aeruginosa when infection occurs early in life.
Figures



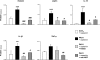
References
-
- Arend WP, Palmer G, Gabay C. IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev 223: 20–38, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Auais A, Adkins B, Napchan G, Piedimonte G. Immunomodulatory effects of sensory nerves during respiratory syncytial virus infection in rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L105–L113, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw 17: 4–12, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Buck H, Winter J. K252a modulates the expression of nerve growth factor-dependent capsaicin sensitivity and substance P levels in cultured adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Neurochem 67: 345–351, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

