MARCKS-related peptide modulates in vivo the secretion of airway Muc5ac
- PMID: 20543006
- PMCID: PMC2951072
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00067.2010
MARCKS-related peptide modulates in vivo the secretion of airway Muc5ac
Retraction in
-
Retraction.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Oct 1;309(7):L750. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.zh5-6863-retr.2015. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26429905 Free PMC article.
Abstract
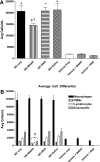
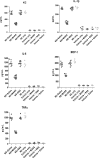
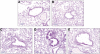
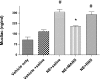
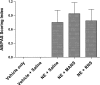
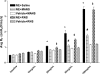
In a mouse model of neutrophil elastase-induced bronchitis that exhibits goblet cell metaplasia and inflammation, we investigated the effects of intratracheal instillation of the MANS peptide, a peptide identical to the NH(2) terminus of the myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) on mucin protein airway secretion, inflammation, and airway reactivity. To induce mucus cell metaplasia in the airways, male BALB/c mice were treated repetitively with the serine protease, neutrophil elastase, on days 1, 4, and 7. On day 11, when goblet cell metaplasia was fully developed and profiles of proinflammatory cytokines were maximal, the animals were exposed to aerosolized methacholine after intratracheal instillation of MANS or a missense control peptide (RNS). MANS, but not RNS, attenuated the methacholine-stimulated secretion of the major respiratory mucin protein, Muc5ac (50% reduction). Concurrently, elastase-induced proinflammatory cytokines typically recovered in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), including KC, IL-1beta, IL-6, MCP-1, and TNFalpha, were reduced by the MANS peptide (mean levels decreased 50-60%). Secondary to the effects of MANS on mucin secretion and inflammation, mechanical lung function by forced oscillation technique was characterized with respect to airway reactivity in response to cumulative aerosol stimulation with serotonin. The MANS peptide was also found to effectively attenuate airway hyperresponsiveness to serotonin in this airway hypersecretory model. Collectively, these findings support the concept that even in airway epithelia remodeled with goblet cell metaplasia and in a state of mucin hypersecretion, exogenous attenuation of function of MARCKS protein via the MANS peptide decreases airway mucin secretion, inflammation, and hyperreactivity.
Figures
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2019 Nov 7;84(216):60097-60098. Fed Regist. 2019. PMID: 37547121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Rengarajan S, Adler KB, Ram A, Ghosh B, Fahim M, Dickey BF. Inhibition of mucin secretion with MARCKS-related peptide improves airway obstruction in a mouse model of asthma. J Appl Physiol 102: 399–405, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Alimam MZ, Piazza FM, Selby DM, Letwin N, Huang L, Rose MC. Muc-5/5ac mucin messenger RNA and protein expression is a marker of goblet cell metaplasia in murine airways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 22: 253–260, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Davis CW, Dickey BF. Regulated airway goblet cell mucin secretion. Annu Rev Physiol 70: 487–512, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Eckert BS, Sharief Y, Crews AL, Adler KB, Jones SL. A peptide against the N-terminus of MARCKS protein attenuates leukocyte migration. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42: 586–94, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

