Decreasing trend of overlapping multilocus sequence types between human and chicken Campylobacter jejuni isolates over a decade in Finland
- PMID: 20543048
- PMCID: PMC2916457
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00581-10
Decreasing trend of overlapping multilocus sequence types between human and chicken Campylobacter jejuni isolates over a decade in Finland
Abstract
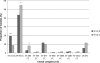
We describe the long-term multilocus sequence typing (MLST) analysis of the population structure and dynamics of 454 Finnish human Campylobacter jejuni isolates, as well as 208 chicken isolates, collected during the mid-1990s to 2007. The sequence type clonal complexes (ST CC) ST-45 CC, ST-21 CC, and ST-677 CC were the most common ones found among all isolates, and they covered 73.9% of all isolates. The ST-283 CC also was found frequently among chicken isolates (8.2%). The predominant STs among all isolates were ST-45, ST-50, and ST-677. ST-137 and ST-230 were common among human isolates, and ST-267 was found more frequently among chicken isolates than human isolates. The ST-45 CC was significantly associated with chicken isolates (P < 0.01), whereas the ST-21 CC was associated with human isolates (P < 0.001). The ST-677 CC was not associated with any host (P = 0.5), and an opposite temporary trend of this complex was seen among chicken and human isolates, with an increase in the former and a decrease in the latter during the study period. Furthermore, the ST-22 and ST-48 CCs were significantly associated with human isolates (P < 0.01), but neither of the CCs was found in chicken isolates. The annual overlap between STs from human and chicken isolates decreased from 76% at the beginning of the study to 58% at the end. Our results suggest that the importance of chicken as a reservoir for strains associated with human infections has declined despite the consumption of domestic chicken meat increasing during the follow-up period by 83%.
Figures
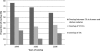
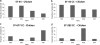
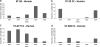
Similar articles
-
Epidemiological relationships of Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from humans and chickens in South Korea.J Microbiol. 2017 Jan;55(1):13-20. doi: 10.1007/s12275-017-6308-8. Epub 2016 Dec 30. J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28035601
-
Multilocus sequence typing of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from humans, chickens, raw milk, and environmental water in Quebec, Canada.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Oct;46(10):3404-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00042-08. Epub 2008 Aug 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18701662 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and whole-genome MLST of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from human infections in three districts during a seasonal peak in Finland.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Dec;52(12):4147-54. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01959-14. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25232158 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogonal typing methods identify genetic diversity among Belgian Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated over a decade from poultry and cases of sporadic human illness.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 Jun 20;275:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29649751
-
Tracing isolates from domestic human Campylobacter jejuni infections to chicken slaughter batches and swimming water using whole-genome multilocus sequence typing.Int J Food Microbiol. 2016 Jun 2;226:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 20. Int J Food Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27041390
Cited by
-
Evolution and comparative genomics of Campylobacter jejuni ST-677 clonal complex.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Sep 4;6(9):2424-38. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu194. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25193305 Free PMC article.
-
Increased risk for Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli infection of pet origin in dog owners and evidence for genetic association between strains causing infection in humans and their pets.Epidemiol Infect. 2013 Dec;141(12):2526-35. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813000356. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Epidemiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23445833 Free PMC article.
-
MLST-based genetic relatedness of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens and humans in Poland.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0226238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226238. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31978059 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Campylobacter jejuni Cj0859c gene (fspA) variants with different C. jejuni multilocus sequence types.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Oct;76(20):6942-3. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01605-10. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20729319 Free PMC article.
-
Monomorphic genotypes within a generalist lineage of Campylobacter jejuni show signs of global dispersion.Microb Genom. 2016 Oct 21;2(10):e000088. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000088. eCollection 2016 Oct. Microb Genom. 2016. PMID: 28348829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Food Safety Authority. 2010. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses in the EU, 2008. EFSA J. 8:1503-1599.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

