Enhancement of antiviral immunity by small molecule antagonist of suppressor of cytokine signaling
- PMID: 20543109
- PMCID: PMC3031960
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902895
Enhancement of antiviral immunity by small molecule antagonist of suppressor of cytokine signaling
Abstract
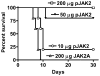
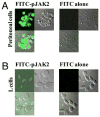
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCSs) are negative regulators of both innate and adaptive immunity via inhibition of signaling by cytokines such as type I and type II IFNs. We have developed a small peptide antagonist of SOCS-1 that corresponds to the activation loop of JAK2. SOCS-1 inhibits both type I and type II IFN activities by binding to the kinase activation loop via the kinase inhibitory region of the SOCS. The antagonist, pJAK2(1001-1013), inhibited the replication of vaccinia virus and encephalomyocarditis virus in cell culture, suggesting that it possesses broad antiviral activity. In addition, pJAK2(1001-1013) protected mice against lethal vaccinia and encephalomyocarditis virus infection. pJAK2(1001-1013) increased the intracellular level of the constitutive IFN-beta, which may play a role in the antagonist antiviral effect at the cellular level. Ab neutralization suggests that constitutive IFN-beta may act intracellularly, consistent with recent findings on IFN-gamma intracellular signaling. pJAK2(1001-1013) also synergizes with IFNs as per IFN-gamma mimetic to exert a multiplicative antiviral effect at the level of transcription, the cell, and protection of mice against lethal viral infection. pJAK2(1001-1013) binds to the kinase inhibitory region of both SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 and blocks their inhibitory effects on the IFN-gamma activation site promoter. In addition to a direct antiviral effect and synergism with IFN, the SOCS antagonist also exhibits adjuvant effects on humoral and cellular immunity as well as an enhancement of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid activation of TLR3. The SOCS antagonist thus presents a novel and effective approach to enhancement of host defense against viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
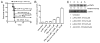
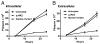
References
-
- Moss B. Poxviridae. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 3. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2007. pp. 2905–2945.
-
- Smith GL, McFadden G. Smallpox: anything to declare? Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:521–527. - PubMed
-
- Moss B, Shisler JL. Immunology 101 at poxvirus U: immune evasion genes. Semin Immunol. 2001;13:59–66. - PubMed
-
- Alcamí A, Smith GL. The vaccinia virus soluble interferon-gamma receptor is a homodimer. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:545–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

