The transwall gradient across the mouse colonic circular muscle layer is carbon monoxide dependent
- PMID: 20543114
- PMCID: PMC2996917
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-156232
The transwall gradient across the mouse colonic circular muscle layer is carbon monoxide dependent
Abstract
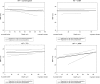
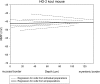
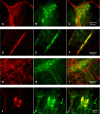
Gastric and small intestinal circular smooth muscle layers have a transwall resting membrane potential (RMP) gradient that is dependent on release of carbon monoxide (CO) from interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs). Our aim was to determine whether a RMP gradient exists in the mouse colon and whether the gradient is CO dependent. Microelectrodes were used to record RMPs from muscle cells at different depths of the circular muscle layer from wild-type and heme oxygenase-2-knockout (HO-2-KO) mice. A transwall RMP gradient was present in wild-type mice. The CO scavenger oxyhemoglobin (20 μM) and the heme oxygenase inhibitor chromium mesoporphyrin IX (CrMP, 5 μM) abolished the transwall gradient. The gradient was absent in HO-2-KO mice. Tetrodotoxin (1 μM) caused a significant depolarization in circular smooth muscle cells throughout the circular muscle layer and abolished the transwall gradient. Removal of the submucosal neurons abolished the gradient. The majority of submucosal neurons contained HO-2 immunoreactivity (HO-2-IR), while ICCs did not. These data show for the first time that a transwall gradient exists across the circular smooth muscle layer of the mouse colon, that the gradient is due to CO, and that the source of CO is the submucosal neurons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane potential gradient is carbon monoxide-dependent in mouse and human small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):G438-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00037.2007. Epub 2007 May 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17510199
-
Effect of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on the transwall gradient of the mouse colon circular smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;592(5):1077-89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.266841. Epub 2013 Dec 23. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24366262 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon monoxide produced by HO-1 upregulation is the main factor behind the abnormal motility seen in experimental ulcerative colitis in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025 Mar 1;328(3):G311-G322. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00179.2023. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39925143
-
Heme oxygenase, carbon monoxide, and interstitial cells of Cajal.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Dec 1;47(5):321-4. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19991201)47:5<321::AID-JEMT3>3.0.CO;2-J. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10602291 Review.
-
Carbon monoxide is an endogenous hyperpolarizing factor in the gastrointestinal tract.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004 Apr;16 Suppl 1:81-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-3150.2004.00480.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004. PMID: 15066010 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of gasotransmitters in neonatal physiology.Nitric Oxide. 2020 Feb 1;95:29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Nitric Oxide. 2020. PMID: 31870965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of inhibitory co-transmission, membrane potential and pacemaker activity determine neuromyogenic function in the rat colon.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Dec;466(12):2305-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1500-8. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24658973
-
Two independent networks of interstitial cells of cajal work cooperatively with the enteric nervous system to create colonic motor patterns.Front Neurosci. 2011 Aug 5;5:93. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00093. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21833164 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide selectively potentiates central preganglionic fast nicotinic synaptic input in mouse superior mesenteric ganglion.J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 31;33(31):12638-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4429-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23904600 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking Gut Motility in Organ and Cultures.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2644:449-466. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3052-5_29. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37142940
References
-
- Smith T. K., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. (1987) Interaction of two electrical pacemakers in muscularis of canine proximal colon. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 252, C290–C299 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

