Myosin II isoforms identify distinct functional modules that support integrity of the epithelial zonula adherens
- PMID: 20543839
- PMCID: PMC3428211
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2072
Myosin II isoforms identify distinct functional modules that support integrity of the epithelial zonula adherens
Abstract
Classic cadherin receptors cooperate with regulators of the actin cytoskeleton to control tissue organization in health and disease. At the apical junctions of epithelial cells, the cadherin ring of the zonula adherens (ZA) couples with a contiguous ring of actin filaments to support morphogenetic processes such as tissue integration and cellular morphology. However, the molecular mechanisms that coordinate adhesion and cytoskeleton at these junctions are poorly understood. Previously we identified non-muscle myosin II as a target of Rho signalling that supports cadherin junctions in mammalian epithelial cells. Myosin II has various cellular functions, which are increasingly attributable to the specific biophysical properties and regulation of its different isoforms. Here we report that myosin II isoforms have distinct and necessary roles at cadherin junctions. Although two of the three mammalian myosin II isoforms are found at the ZA, their localization is regulated by different upstream signalling pathways. Junctional localization of myosin IIA required E-cadherin adhesion, Rho/ROCK and myosin light-chain kinase, whereas junctional myosin IIB depended on Rap1. Further, these myosin II isoforms support E-cadherin junction integrity by different mechanisms. Myosin IIA RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) selectively perturbed the accumulation of E-cadherin in the apical ZA, decreased cadherin homophilic adhesion and disrupted cadherin clustering. In contrast, myosin IIB RNAi decreased filament content, altered dynamics, and increased the lateral movement of the perijunctional actin ring. Myosin IIA and IIB therefore identify two distinct functional modules, with different upstream signals that control junctional localization, and distinct functional effects. We propose that these two isoform-based modules cooperate to coordinate adhesion receptor and F-actin organization to form apical cadherin junctions.
Figures
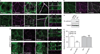
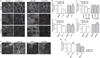
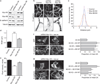
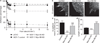
Comment in
-
Hold on tightly, let go lightly: myosin functions at adherens junctions.Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;12(7):633-5. doi: 10.1038/ncb0710-633. Nat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20596044 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Multicomponent analysis of junctional movements regulated by myosin II isoforms at the epithelial zonula adherens.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022458. Epub 2011 Jul 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799860 Free PMC article.
-
An RPTPα/Src family kinase/Rap1 signaling module recruits myosin IIB to support contractile tension at apical E-cadherin junctions.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Apr 1;26(7):1249-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-07-1223. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25631816 Free PMC article.
-
Tension-sensitive actin assembly supports contractility at the epithelial zonula adherens.Curr Biol. 2014 Aug 4;24(15):1689-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.028. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 25065757 Free PMC article.
-
Unique and redundant functions of cytoplasmic actins and nonmuscle myosin II isoforms at epithelial junctions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022 Sep;1515(1):61-74. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14808. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022. PMID: 35673768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A central role for cadherin signaling in cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Sep 1;358(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28412244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zonula occludens-1 and -2 regulate apical cell structure and the zonula adherens cytoskeleton in polarized epithelia.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Feb;23(4):577-90. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-09-0791. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22190737 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level Force-dependent Allosteric Enhancement of αE-catenin Binding to F-actin by Vinculin.J Mol Biol. 2023 Mar 1;435(5):167969. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.167969. Epub 2023 Jan 20. J Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36682678 Free PMC article.
-
Hold on tightly, let go lightly: myosin functions at adherens junctions.Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;12(7):633-5. doi: 10.1038/ncb0710-633. Nat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20596044 Free PMC article.
-
Cell wound repair in Drosophila occurs through three distinct phases of membrane and cytoskeletal remodeling.J Cell Biol. 2011 May 2;193(3):455-64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201011018. Epub 2011 Apr 25. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21518790 Free PMC article.
-
Muscular anatomy of the Podocoryna carnea hydrorhiza.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 14;8(8):e72221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072221. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yonemura S, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S. Cell-to-cell adherens junction formation and actin filament organization: similarities and differences between non-polarized fibroblasts and polarized epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 1995;108:127–142. - PubMed
-
- Vaezi A, Bauer C, Vasioukhin V, Fuchs E. Actin cable dynamics and Rho/ROCK orchestrate a polarized cytoskeletal architecture in the early steps of assembling a stratified epithelium. Dev. Cell. 2002;3:367–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

