Synaptic plasticity, a symphony in GEF
- PMID: 20543890
- PMCID: PMC2882301
- DOI: 10.1021/cn100012x
Synaptic plasticity, a symphony in GEF
Abstract
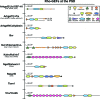
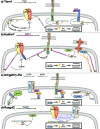
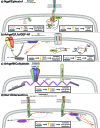
Dendritic spines are the postsynaptic sites for the majority of excitatory synapses in the mammalian forebrain. While many spines display great stability, others change shape in a matter of seconds to minutes. These rapid alterations in dendritic spine number and size require tight control of the actin cytoskeleton, the main structural component of dendritic spines. The ability of neurons to alter spine number and size is essential for the expression of neuronal plasticity. Within spines, guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) act as critical regulators of the actin cytoskeleton by controlling the activity of Rho-GTPases. In this review we focus on the Rho-GEFs expressed in the nucleus accumbens and localized to the postsynaptic density, and thus positioned to effect rapid alterations in the structure of dendritic spines. We review literature that ties these GEFs to different receptor systems and intracellular signaling cascades and discuss the effects these interactions are likely to have on synaptic plasticity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Asef2 promotes dendritic spine formation via Rac activation and spinophilin-dependent targeting.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10295-308. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605543. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25750125 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Rho GEFs in synaptic physiology and behavior.Neuroscientist. 2013 Jun;19(3):255-73. doi: 10.1177/1073858413475486. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Neuroscientist. 2013. PMID: 23401188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of synapse development and plasticity by Rho GTPase regulatory proteins.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Jul;94(2):133-48. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21530608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44: a novel synaptic cell adhesion molecule regulating structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Dec 15;27(25):4055-4066. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-06-0423. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27798233 Free PMC article.
-
Kalirin-7 is necessary for normal NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity.BMC Neurosci. 2011 Dec 19;12:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-126. BMC Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22182308 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The adhesion-GPCR BAI1 regulates synaptogenesis by controlling the recruitment of the Par3/Tiam1 polarity complex to synaptic sites.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 17;33(16):6964-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3978-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23595754 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 is a downstream effector of PKCα in structural synaptic plasticity.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 4;10(1):1777. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58610-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32019972 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders.Rev Neurosci. 2011;22(5):535-49. doi: 10.1515/RNS.2011.044. Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21967517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin 18Aα targets the guanine nucleotide exchange factor β-Pix to the dendritic spines of cerebellar Purkinje neurons and promotes spine maturation.FASEB J. 2021 Jan;35(1):e21092. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001449R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33378124 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for spatiotemporal regulation of Rho-GTPase signaling at synapses.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Aug 5;601:4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.05.034. Epub 2015 May 21. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 26003445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nimchinsky E. A.; Sabatini B. L.; Svoboda K. (2002) Structure and function of dendritic spines. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 313–353. - PubMed
-
- Holtmaat A.; Svoboda K. (2009) Experience-dependent structural synaptic plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 647–658. - PubMed
-
- Bourne J.; Harris K. M. (2007) Do thin spines learn to be mushroom spines that remember?. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 17, 381–386. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

