Control growth factor release using a self-assembled [polycation:heparin] complex
- PMID: 20543985
- PMCID: PMC2882380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011017
Control growth factor release using a self-assembled [polycation:heparin] complex
Abstract
The importance of growth factors has been recognized for over five decades; however their utilization in medicine has yet to be fully realized. This is because free growth factors have short half-lives in plasma, making direct injection inefficient. Many growth factors are anchored and protected by sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the body. We set out to explore the use of heparin, a well-characterized sulfated glycosaminoglycan, for the controlled release of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). Heparin binds a multitude of growth factors and maintains their bioactivity for an extended period of time. We used a biocompatible polycation to precipitate out the [heparin:FGF-2] complex from neutral buffer to form a release matrix. We can control the release rate of FGF-2 from the resultant matrix by altering the molecular weight of the polycation. The FGF-2 released from the delivery complex maintained its bioactivity and initiated cellular responses that were at least as potent as fresh bolus FGF-2 and fresh heparin stabilized FGF-2. This new delivery platform is not limited to FGF-2 but applicable to the large family of heparin-binding growth factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

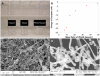

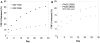
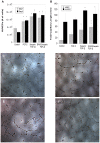
Similar articles
-
A [polycation:heparin] complex releases growth factors with enhanced bioactivity.J Control Release. 2011 Mar 10;150(2):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.11.025. Epub 2010 Nov 29. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21118705
-
Hyaluronate-heparin conjugate gels for the delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2).J Biomed Mater Res. 2002 Oct;62(1):128-35. doi: 10.1002/jbm.10238. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002. PMID: 12124794
-
Crystal structure of fibroblast growth factor receptor ectodomain bound to ligand and heparin.Nature. 2000 Oct 26;407(6807):1029-34. doi: 10.1038/35039551. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11069186
-
Diversity does make a difference: fibroblast growth factor-heparin interactions.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Oct;8(5):578-86. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80147-4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9818261 Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor-2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;32(2):115-20. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(99)00123-5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10687947 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo vascularization of MSC-loaded porous hydroxyapatite constructs coated with VEGF-functionalized collagen/heparin multilayers.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 22;6:19871. doi: 10.1038/srep19871. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26794266 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic angiogenesis: controlled delivery of angiogenic factors.Ther Deliv. 2012 Jun;3(6):693-714. doi: 10.4155/tde.12.50. Ther Deliv. 2012. PMID: 22838066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlled Delivery of Stem Cell-Derived Trophic Factors Accelerates Kidney Repair After Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Sep;8(9):959-970. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0222. Epub 2019 May 30. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31144785 Free PMC article.
-
Towards comprehensive cardiac repair and regeneration after myocardial infarction: Aspects to consider and proteins to deliver.Biomaterials. 2016 Mar;82:94-112. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.12.025. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 26757257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered hydrogels for peripheral nerve repair.Mater Today Bio. 2023 May 19;20:100668. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100668. eCollection 2023 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37273791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coultas L, Chawengsaksophak K, Rossant J. Endothelial cells and VEGF in vascular development. Nature. 2005;438:937–945. - PubMed
-
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987;237:1154–1162. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7709–7712. - PubMed
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, et al., editors. The Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4 ed. New York, NY: Garland Science; 2002. 1616
-
- Guler HP, Zapf J, Schmid C, Froesch ER. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989;121:753–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

