Astrocyte hypoxic response is essential for pathological but not developmental angiogenesis of the retina
- PMID: 20544853
- PMCID: PMC2993327
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.20997
Astrocyte hypoxic response is essential for pathological but not developmental angiogenesis of the retina
Abstract
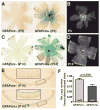
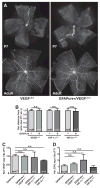
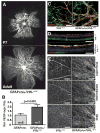
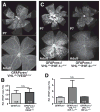
Vascular/parenchymal crosstalk is increasingly recognized as important in the development and maintenance of healthy vascularized tissues. The retina is an excellent model in which to study the role of cell type-specific contributions to the process of blood vessel and neuronal growth. During retinal vascular development, glial cells such as astrocytes provide the template over which endothelial cells migrate to form the retinal vascular network, and hypoxia-regulated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been demonstrated to play a critical role in this process as well as pathological neovascularization. To investigate the nature of cell-specific contributions to this process, we deleted VEGF and its upstream regulators, the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha, and the negative regulator of HIF alpha, von Hippel-Lindau protein (VHL), in astrocytes. We found that loss of hypoxic response and VEGF production in astrocytes does not impair normal development of retinal vasculature, indicating that astrocyte-derived VEGF is not essential for this process. In contrast, using a model of oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy, we show that astrocyte-derived VEGF is essential for hypoxia-induced neovascularization. Thus, we demonstrate that astrocytes in the retina have highly divergent roles during developmental, physiological angiogenesis, and ischemia-driven, pathological neovascularization.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aiello LP, Pierce EA, Foley ED, Takagi H, Chen H, Riddle L, Ferrara N, King GL, Smith LE. Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF-receptor chimeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(23):10457–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe’er J, Stone J, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med. 1995;1(10):1024–8. - PubMed
-
- Arjamaa O, Nikinmaa M. Oxygen-dependent diseases in the retina: role of hypoxia-inducible factors. Exp Eye Res. 2006;83(3):473–83. - PubMed
-
- Banin E, Dorrell MI, Aguilar E, Ritter MR, Aderman CM, Smith AC, Friedlander J, Friedlander M. T2-TrpRS inhibits preretinal neovascularization and enhances physiological vascular regrowth in OIR as assessed by a new method of quantification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(5):2125–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

