Quadriceps low-frequency fatigue and muscle pain are contraction-type-dependent
- PMID: 20544933
- PMCID: PMC2989463
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.21679
Quadriceps low-frequency fatigue and muscle pain are contraction-type-dependent
Abstract
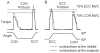
Eccentric contractions are thought to induce greater low-frequency fatigue (LFF) and delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) than concentric contractions. In this study we induced a similar amount of eccentric quadriceps muscle fatigue during either a concentric or eccentric fatigue task to compare LFF and DOMS. Subjects (n = 22) performed concentric or eccentric fatigue tasks using 75% of the pre-fatigue maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) torque, and both tasks ended when the MVC eccentric torque decreased by 25% pre-fatigue. When subjects reached the failure criterion during the eccentric and concentric tasks, the concentric MVC was 78 +/- 9.8% and 64 +/- 8.4% of initial, respectively. LFF was greater after the concentric than the eccentric protocols (22 +/- 12.4% and 15 +/- 7.6% increase, respectively; P < 0.01). DOMS was over 100% greater for the eccentric protocol. These results indicate that DOMS is not dependent on the events that contribute to LFF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Fitts RH. Cellular mechanisms of muscle fatigue. Physiol Rev. 1994;74:49–94. - PubMed
-
- Gandevia SC. Spinal and supraspinal factors in human muscle fatigue. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1725–1789. - PubMed
-
- Bigland-Ritchie B, Rice CL, Garland SJ, Walsh ML. Task-dependent factors in fatigue of human voluntary contractions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;384:361–380. - PubMed
-
- Enoka RM, Stuart DG. Neurobiology of muscle fatigue. J Appl Physiol. 1992;72:1631–1648. - PubMed
-
- Baudry S, Klass M, Pasquet B, Duchateau J. Age-related fatigability of the ankle dorsiflexor muscles during concentric and eccentric contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007;100:515–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

