Effects of pramipexole on impulsive choice in male wistar rats
- PMID: 20545391
- PMCID: PMC3021944
- DOI: 10.1037/a0019244
Effects of pramipexole on impulsive choice in male wistar rats
Abstract
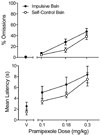
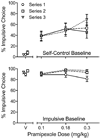
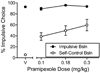
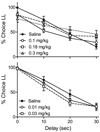
Clinical reports, primarily with Parkinson's disease patients, note an association between the prescribed use of pramipexole (and other direct-acting dopamine agonist medications) and impulse control disorders, particularly pathological gambling. Two experiments examined the effects of acute pramipexole on rats' impulsive choices where impulsivity was defined as selecting a smaller-sooner over a larger-later food reward. In Experiment 1, pramipexole (0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg) significantly increased impulsive choices in a condition in which few impulsive choices were made during a stable baseline. In a control condition, in which impulsive choices predominated during baseline, pramipexole did not significantly change the same rats' choices. Experiment 2 explored a wider range of doses (0.01 to 0.3 mg/kg) using a choice procedure in which delays to the larger-later reinforcer delivery increased across trial blocks within each session. At the doses used in Experiment 1, pramipexole shifted choice toward indifference regardless of the operative delay. At lower doses of pramipexole (0.01 and 0.03 mg/kg), a trend toward more impulsive choice was observed at the 0.03 mg/kg dose. The difference in outcomes across experiments may be due to the more complex discriminations required in Experiment 2, that is, multiple discriminations between changing delays within each session.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of acute pramipexole on male rats' preference for gambling-like rewards II.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Jun;20(3):167-72. doi: 10.1037/a0027117. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22288460 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acute pramipexole on preference for gambling-like schedules of reinforcement in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Jan;213(1):11-8. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2006-5. Epub 2010 Sep 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20814781 Free PMC article.
-
Pramipexole-induced disruption of behavioral processes fundamental to intertemporal choice.J Exp Anal Behav. 2013 May;99(3):290-317. doi: 10.1002/jeab.21. Epub 2013 Feb 22. J Exp Anal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23436721 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine-agonists and impulsivity in Parkinson's disease: impulsive choices vs. impulsive actions.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Jun;35(6):2499-506. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22344. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 24038587 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive impulsivity in animal models: role of response time and reinforcing rate in delay intolerance with two-choice operant tasks.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Mar-Apr;58(4-5):694-701. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.11.007. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19945469 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Slot-Machine Reward Schedules Induce Gambling Addiction in Rats?J Gambl Stud. 2019 Sep;35(3):887-914. doi: 10.1007/s10899-019-09852-1. J Gambl Stud. 2019. PMID: 31049772
-
Effects of acute pramipexole on male rats' preference for gambling-like rewards II.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Jun;20(3):167-72. doi: 10.1037/a0027117. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22288460 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting drug effects in preclinical models of impulsive choice: emphasis on glutamatergic compounds.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Mar;235(3):607-626. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4825-0. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29305628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delay discounting in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice: adolescent-limited and life-persistent patterns of impulsivity.Behav Neurosci. 2011 Apr;125(2):194-201. doi: 10.1037/a0022919. Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21463022 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of implicit and explicit reward learning in low risk alcohol users versus people who binge drink and people with alcohol dependence.Addict Behav Rep. 2019 Mar 29;9:100178. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2019.100178. eCollection 2019 Jun. Addict Behav Rep. 2019. PMID: 31193786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi SM, Petry NM. Pathological gambling severity is associated with impulsivity in a delay discounting procedure. Behavioural Processes. 2003;64:345–354. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed., text rev. Washington, DC.: Author; 2000.
-
- Bennett JP, Piercey MF. Pramipexole -- a new dopamine agonist for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurological Science. 1999;163:23, 31. - PubMed

