Extracellular domain dependence of PTPalpha transforming activity
- PMID: 20545765
- PMCID: PMC4876864
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01410.x
Extracellular domain dependence of PTPalpha transforming activity
Abstract
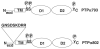
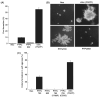
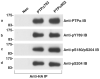
Two isoforms of the transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPalpha, which differ by nine amino acids in their extracellular regions, are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. Over-expression of the shorter isoform transforms rodent cells, and it has previously been reasonable to assume that this was a direct consequence of its dephosphorylation and activation of Src. Transformation by the longer wild-type isoform has not previously been studied. We tested the activities of both isoforms in NIH3T3 cells and found that, while both dephosphorylated and activated Src similarly, only the shorter isoform induced focus formation or anchorage-independent growth. Differences in phosphorylation of PTPalpha at its known regulatory sites, Grb2 binding to PTPalpha, phosphorylation level of focal adhesion kinase by PTPalpha, or overall localization were excluded as possible explanations for the differences in transforming activities. The results suggest that transformation by PTPalpha involves at least one function other than, or in addition to, its activation of Src and that this depends on PTPalpha's extracellular domain. Previous studies have suggested that PTPalpha might be a useful target in breast and colon cancer therapy, and the results presented here suggest that it may be advantageous to develop isoform-specific therapeutic reagents.
Figures
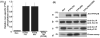

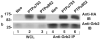
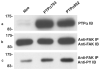
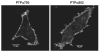
References
-
- Ardini E, Agresti R, Tagliabue E, Greco M, Aiello P, Yang LT, Menard S, Sap J. Expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase α (RPTPα) in human breast cancer correlates with low tumor grade, and inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2000;19:4979–4987. - PubMed
-
- Autero M, Saharinen J, Pessa-Morikawa T, Soula-Rothhut M, Oetken C, Gassmann M, Bergman M, Alitalo K, Burn P, Gahmberg CG, Mustelin T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase by p50csk kinase creates a binding site for p56lck tyrosine kinase and activates the phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994;14:1308–1321. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunton VG, Ozanne BW, Paraskeva C, Frame MC. A role for epidermal growth factor receptor, c-Src and focal adhesion kinase in an in vitro model for the progression of colon cancer. Oncogene. 1997;14:283–293. - PubMed
-
- Buist A, Blanchetot C, Tertoolen LG, den Hertog J. Identification of p130cas as an in vivo substrate of receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase α. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:20754–20761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

