Zebrafish class 1 phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins: PITPbeta and double cone cell outer segment integrity in retina
- PMID: 20545905
- PMCID: PMC2919645
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01085.x
Zebrafish class 1 phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins: PITPbeta and double cone cell outer segment integrity in retina
Abstract
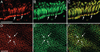
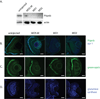
Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) in yeast co-ordinate lipid metabolism with the activities of specific membrane trafficking pathways. The structurally unrelated metazoan PITPs (mPITPs), on the other hand, are an under-investigated class of proteins. It remains unclear what biological activities mPITPs discharge, and the mechanisms by which these proteins function are also not understood. The soluble class 1 mPITPs include the PITPalpha and PITPbeta isoforms. Of these, the beta-isoforms are particularly poorly characterized. Herein, we report the use of zebrafish as a model vertebrate for the study of class 1 mPITP biological function. Zebrafish express PITPalpha and PITPbeta-isoforms (Pitpna and Pitpnb, respectively) and a novel PITPbeta-like isoform (Pitpng). Pitpnb expression is particularly robust in double cone cells of the zebrafish retina. Morpholino-mediated protein knockdown experiments demonstrate Pitpnb activity is primarily required for biogenesis/maintenance of the double cone photoreceptor cell outer segments in the developing retina. By contrast, Pitpna activity is essential for successful navigation of early developmental programs. This study reports the initial description of the zebrafish class 1 mPITP family, and the first analysis of PITPbeta function in a vertebrate.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Structure of PITPbeta in complex with phosphatidylcholine: comparison of structure and lipid transfer to other PITP isoforms.Biochemistry. 2005 Nov 15;44(45):14760-71. doi: 10.1021/bi051191r. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16274224
-
Ligand and membrane-binding behavior of the phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins PITPα and PITPβ.Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;94(6):528-533. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2015-0152. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27783542
-
Biochemical and biological functions of class I phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jun;1771(6):677-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.03.009. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17490911 Review.
-
Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein beta displays minimal sphingomyelin transfer activity and is not required for biosynthesis and trafficking of sphingomyelin.Biochem J. 2002 Aug 15;366(Pt 1):23-34. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020317. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12023904 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of phosphatidylinositol by phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins.Biochem Soc Symp. 2007;(74):259-71. doi: 10.1042/BSS0740259. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007. PMID: 17233595 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoinositides in Retinal Function and Disease.Cells. 2020 Apr 2;9(4):866. doi: 10.3390/cells9040866. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32252387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian diseases of phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins and their homologs.Clin Lipidol. 2010 Dec 1;5(6):867-897. doi: 10.2217/clp.10.67. Clin Lipidol. 2010. PMID: 21603057 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol synthase is required for lens structural integrity and photoreceptor cell survival in the zebrafish eye.Exp Eye Res. 2011 Oct;93(4):460-74. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.06.010. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Exp Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21722635 Free PMC article.
-
Individual phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins have distinct functions that do not involve lipid transfer activity.Blood Adv. 2023 Aug 22;7(16):4233-4246. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008735. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 36930803 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of phosphatidylinositol transfer protein α ameliorates the pathology of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 6;114(23):6080-6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703556114. Epub 2017 May 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28533404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Irvine RF. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989;341:197–205. - PubMed
-
- Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC. Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:481–507. - PubMed
-
- Majerus PW. Inositol phosphate biochemistry. Annu Rev. Biochem. 1992;61:225–250. - PubMed
-
- Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses. FASEB J. 1995;9:484–496. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

