Moesin-induced signaling in response to lipopolysaccharide in macrophages
- PMID: 20546116
- PMCID: PMC4502922
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01271.x
Moesin-induced signaling in response to lipopolysaccharide in macrophages
Abstract
Background and objective: Many physiological and pathophysiological conditions are attributable in part to cytoskeletal regulation of cellular responses to signals. Moesin (membrane-organizing extension spike protein), an ERM (ezrin, radixin and moesin) family member, is involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated events in mononuclear phagocytes; however, its role in signaling is not fully understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the LPS-induced moesin signaling pathways in macrophages.
Material and methods: Macrophages were stimulated with 500 ng/mL LPS in macrophage serum-free medium. For blocking experiments, cells were pre-incubated with anti-moesin antibody. Moesin total protein and phosphorylation were studied with western blotting. Moesin mRNA was assessed using quantitative real-time PCR. To explore binding of moesin to LPS, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gel shift assay was performed. Moesin immunoprecipitation with CD14, MD-2 and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and co-immunoprecipitation of MyD88-interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and IRAK-tumor necrosis factor receptor-activated factor 6 (TRAF6) were analyzed. Phosphorylation of IRAK and activities of MAPK, nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) and IkappaBalpha were studied. Tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1beta and interferon beta were measured by ELISA.
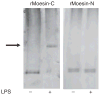
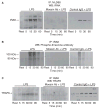
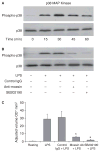
Results: Moesin was identified as part of a protein cluster that facilitates LPS recognition and results in the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates moesin expression and phosphorylation by binding directly to the moesin carboxyl-terminus. Moesin is temporally associated with TLR4 and MD-2 after LPS stimulation, while CD14 is continuously bound to moesin. Lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling is transferred downstream to p38, p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB activation. Blockage of moesin function interrupts the LPS response through an inhibition of MyD88, IRAK and TRAF6, negatively affecting subsequent activation of the MAP kinases (p38 and ERK), NF-kappaB activation and translocation to the nucleus.
Conclusion: These results suggest an important role for moesin in the innate immune response and TLR4-mediated pattern recognition in periodontal disease.
(c) 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Euscaphic acid isolated from roots of Rosa rugosa inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via TLR4-mediated NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1936-46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24062. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22234926
-
Thalidomide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha production via down-regulation of MyD88 expression.Innate Immun. 2009 Feb;15(1):33-41. doi: 10.1177/1753425908099317. Innate Immun. 2009. PMID: 19201823
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
TLR-signaling networks: an integration of adaptor molecules, kinases, and cross-talk.J Dent Res. 2011 Apr;90(4):417-27. doi: 10.1177/0022034510381264. Epub 2010 Oct 12. J Dent Res. 2011. PMID: 20940366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 9;9:1849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01849. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30140268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polysaccharides From Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat Ameliorate Colitis Rats via Regulation of the Metabolic Profiling and NF-κ B/TLR4 and IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 10;9:746. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00746. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30042683 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of membrane-organizing extension spike protein as a biomarker for periodontal disease by comparing its level in gingival crevicular fluid in individuals with and without chronic severe periodontitis - A pilot study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2019 Jul-Aug;23(4):329-333. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_694_18. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2019. PMID: 31367129 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Plasmodium Glycosylphosphatidylinositol and the Host Protein Moesin Has No Implication in Malaria Pathology.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 16;7:183. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00183. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28560184 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA Expression of Ezrin in Gingival Crevicular Fluid and Whole Blood of Gingivitis and Chronic Periodontitis Patients - A Polymerase Chain Reaction Study.Contemp Clin Dent. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):267-273. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_6_21. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Contemp Clin Dent. 2022. PMID: 36213856 Free PMC article.
-
Serum moesin is associated with cognitive impairment and glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Jul 29;17(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01876-5. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40734173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M. ERM proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical actin organization and cell growth signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:104–109. - PubMed
-
- Amieva MR, Furthmayr H. Subcellular localization of moesin in dynamic filopodia, retraction fibers, and other structures involved in substrate exploration, attachment, and cell-cell contacts. Exp Cell Res. 1995;219:180–196. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher A, Edwards K, Fehon RG. ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:586–599. - PubMed
-
- Masumoto J, Sagara J, Hayama M, Hidaka E, Katsuyama T, Taniguchi S. Differential expression of moesin in cells of hematopoietic lineage and lymphatic systems. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998;110:33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

