Nesfatin-1: a novel inhibitory regulator of food intake and body weight
- PMID: 20546141
- PMCID: PMC4079085
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00770.x
Nesfatin-1: a novel inhibitory regulator of food intake and body weight
Abstract
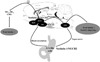
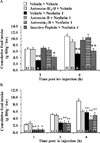
The protein nucleobindin 2 (NUCB2) or NEFA (DNA binding/EF-hand/acidic amino acid rich region) was identified over a decade ago and implicated in intracellular processes. New developments came with the report that post-translational processing of hypothalamic NUCB2 may result in nesfatin-1, nesfatin-2 and nesfatin-3 and convergent studies showing that nesfatin-1 and full length NUCB2 injected in the brain potently inhibit the dark phase food intake in rodents including leptin receptor deficient Zucker rats. Nesfatin-1 also reduces body weight gain, suggesting a role as a new anorexigenic factor and modulator of energy balance. In light of the obesity epidemic and its associated diseases, underlying new mechanisms regulating food intake may be promising targets in the drug treatment of obese patients particularly as the vast majority of them display reduced leptin sensitivity or leptin resistance while nesfatin-1's mechanism of action is leptin independent. Although much progress on the localization of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 in the brain and periphery as well as on the understanding of nesfatin-1's anorexic effect have been achieved during the past three years, several important mechanisms have yet to be unraveled such as the identification of the nesfatin-1 receptor and the regulation of NUCB2 processing and nesfatin-1 release.
© 2010 The Authors. obesity reviews © 2010 International Association for the Study of Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
A.S., M.G and Y.T. have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kanai Y, Tanuma S. Purification of a novel B cell growth and differentiation factor associated with lupus syndrome. Immunol Lett. 1992;32:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Barnikol-Watanabe S, Gross NA, Gotz H, Henkel T, Karabinos A, Kratzin H, Barnikol HU, Hilschmann N. Human protein NEFA, a novel DNA binding/EF-hand/leucine zipper protein. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA, isolation and characterization of the protein. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994;375:497–512. - PubMed
-
- Miura K, Titani K, Kurosawa Y, Kanai Y. Molecular cloning of nucleobindin, a novel DNA-binding protein that contains both a signal peptide and a leucine zipper structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;187:375–380. - PubMed
-
- Karabinos A, Bhattacharya D, Morys-Wortmann C, Kroll K, Hirschfeld G, Kratzin HD, Barnikol-Watanabe S, Hilschmann N. The divergent domains of the NEFA and nucleobindin proteins are derived from an EF-hand ancestor. Mol Biol Evol. 1996;13:990–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

